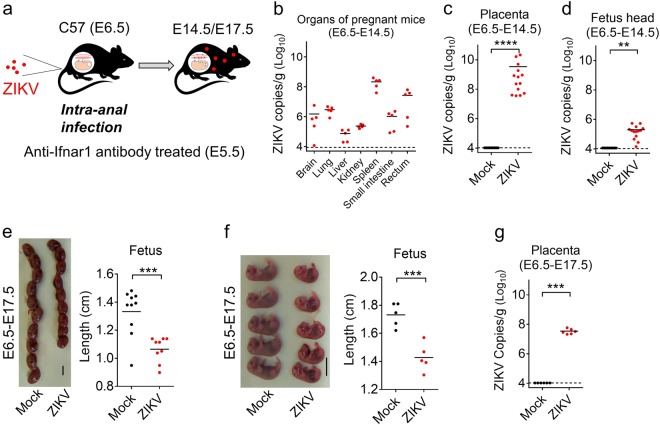
Fig. 5. Intra-anal infection of pregnant mice with ZIKV leads to transplacental transmission and impaired fetal development.
a Illustration of the experiment. 7–8-week-old C57 mice were mated, and pregnant mice were infected i.a. by ZIKV (106 PFU/mouse) at E6.5 after treatment with anti-Ifnar1 antibody at E5.5. Mice were euthanized at E14.5 (E6.5-E14.5) or E17.5 (E6.5-E17.5). b–d ZIKV RNA copies recovered at E14.5 (8 dpi) from tissues of pregnant mice, including the brain, lung, liver, kidney, spleen, small intestine, and rectum (n = 5 per group) (b), or the offspring of 2 representative pregnant mice including the placenta (c) or the fetal head (d) were quantified by qRT-PCR (n = 9, Mock; n = 14). e, f Condition and length of individual fetuses at E17.5 (e n = 10 Mock; n = 9 ZIKV; f n = 5 per group). The size of each fetus within the amniotic sac is shown in (e), while (f) shows the length measured when the placenta and amniotic tissues are removed. Scale bar = 1 cm. g Viral load in the placenta at E17.5 (n = 6 per group). Offspring in (e–g) were from one representative pregnant mouse. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001, unpaired Student’s t-test