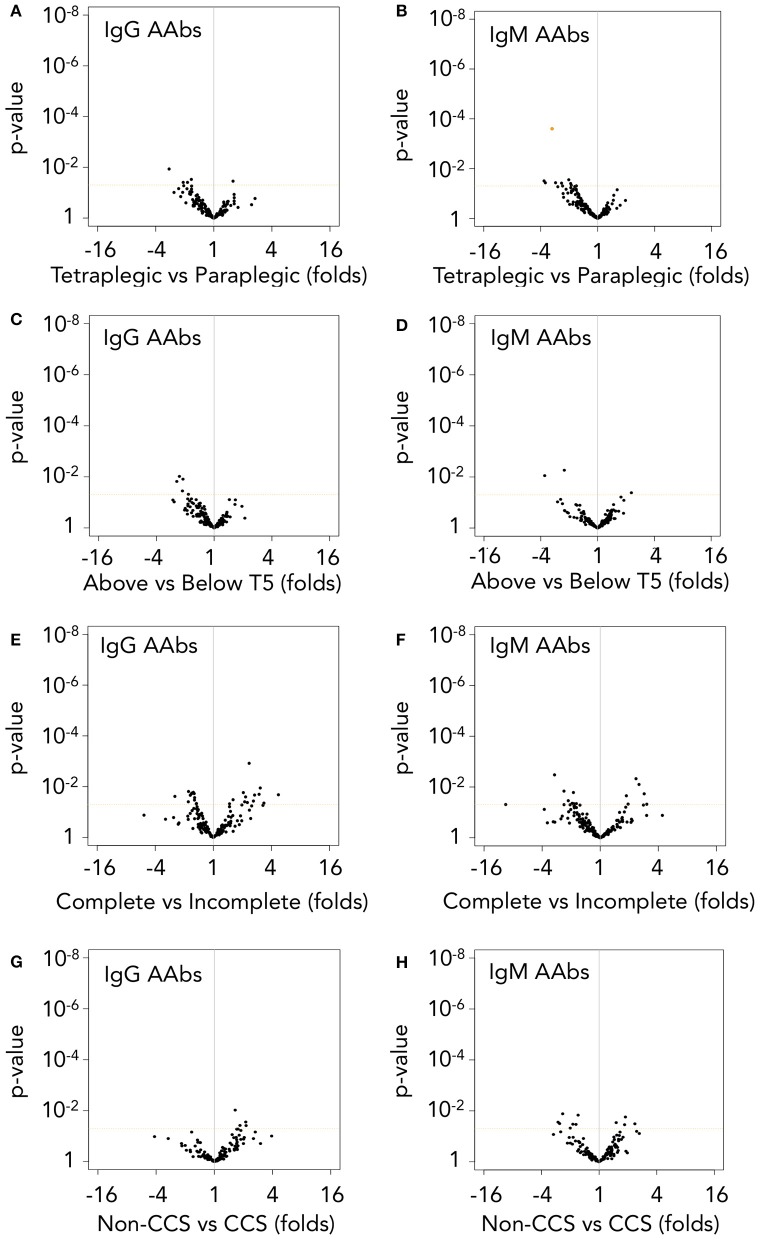
Figure 6.
Autoantibody levels are higher in spinal cord injury patients independently of lesion level and severity. (A,B) IgG and IgM AAb binding are not significantly different after performing t-test (p-value in y-axis) followed by false discovery rate (FDR) correction between tetraplegic and paraplegic patients, but for a single IgM AAb against HBA (orange-filled spot, B). (C,D) However, when classifying patients into those with lesions above or below T5 spinal segment, not a single AAb present different levels between the two groups. (E,F) Complete patients (AIS A) and incomplete patients (AIS B–D) do not show significant differences in IgG nor IgM AAb levels. (G,H) Comparison of cervical AIS D central cord syndrome patients (CCS, a less severe traumatic spinal cord injury) with their counterparts cervical AIS A patients (Non-CCS) also fails to found any statistically significant difference in AAb levels due to lesion severity. Dotted horizontal orange line represents t-test p-value = 0.05. Orange-filled spot represents FDR < 0.05 after multiple comparison correction by Benjamini-Yekutieli method.