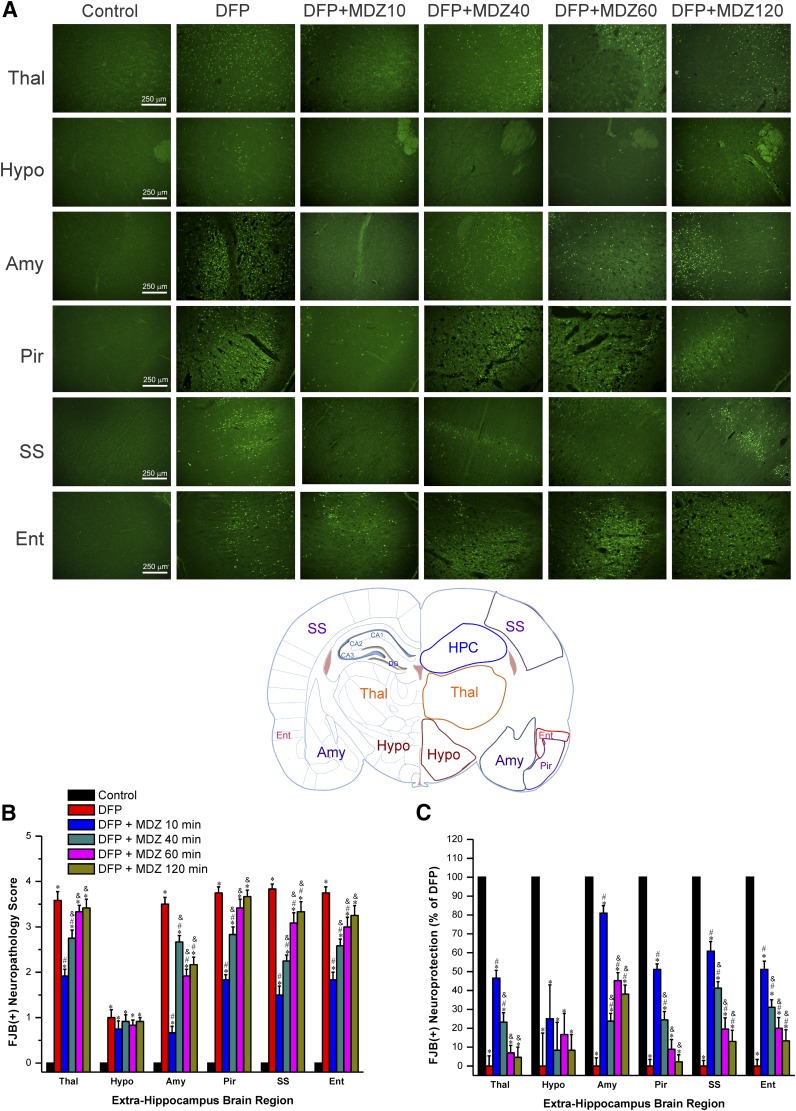
Fig. 5.
Time-course profile of midazolam (2 mg/kg, i.m.) on DFP-induced neuronal injury in various extrahippocampal regions at 3 days after DFP exposure. (A) Representative FJB(+) staining depicting dying neurons in extrahippocampal regions in control and DFP subgroups. Rat brain atlas illustrating the regions selected for analysis of FJB(+) staining, including thalamus (Thal), hypothalamus (Hypo), amygdala (Amy), piriform cortex (Pir), somatosensory cortex (SS), and entorhinal cortex (Ent) regions. (B) The bar charts depict neuropathology scores in these regions and represent severity level of FJB(+) staining dying neurons. DFP exposures was associated with severe damage with high neuropathology score. (C) Normalized percent neuroprotection in extrahippocampal brain regions from rats treated with midazolam at 10–120 minutes after DFP exposure. Normalized neuroprotection was calculated using the untreated DFP-exposed group as the baseline (0% protection). Each bar represents the mean ± S.E.M. (n = 4–11 rats per group). *P < 0.05 versus control (no DFP); #P < 0.05 versus DFP group; &P < 0.05 versus DFP+MDZ 10-minute group (Mann-Whitney U test).