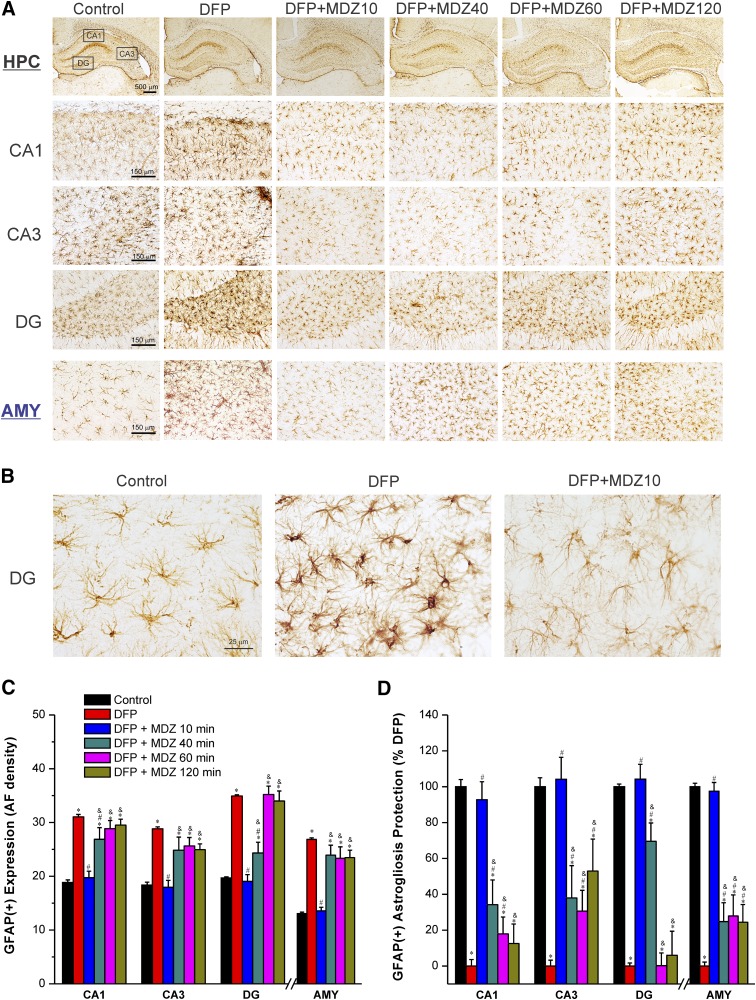
Fig. 8.
Time-course of protective effect of midazolam (2 mg/kg) on DFP-induced GFAP(+) astrocyte neuroinflammation in the hippocampus (HPC) and amygdala (AMY) regions at 3 days after DFP exposure. (A) Representative sections of GFAP(+) immunostaining in the hippocampus and amygdala. (B) A typical reactive astrocyte image includes swollen soma and shorter processes with increased AF density in the hippocampal regions in the untreated DFP group. (C) The bar charts depict the area fractionation (AF) densitometric quantification of GFAP(+) expression in the hippocampal subfields and amygdala. (D) Percentage of protection of GFAP(+) astrogliosis in various subgroups in the hippocampus subfields. Normalized protection of GFAP(+) neuroinflammation is calculated using untreated DFP-exposed group as 0% protection. In this estimate, the control group not exposed to DFP was rated as 100% GFAP(+) expressing astrocytes because of lack of any damaging response in this group in any region. Values represent the mean ± S.E.M. (n = 4–11 rats per group). *P < 0.05 versus control (no DFP); #P < 0.05 versus DFP group; &P < 0.05 versus DFP+MDZ 10-minute group (two-way repeated measures analysis of variance and post hoc Tukey’s honestly significant difference test).