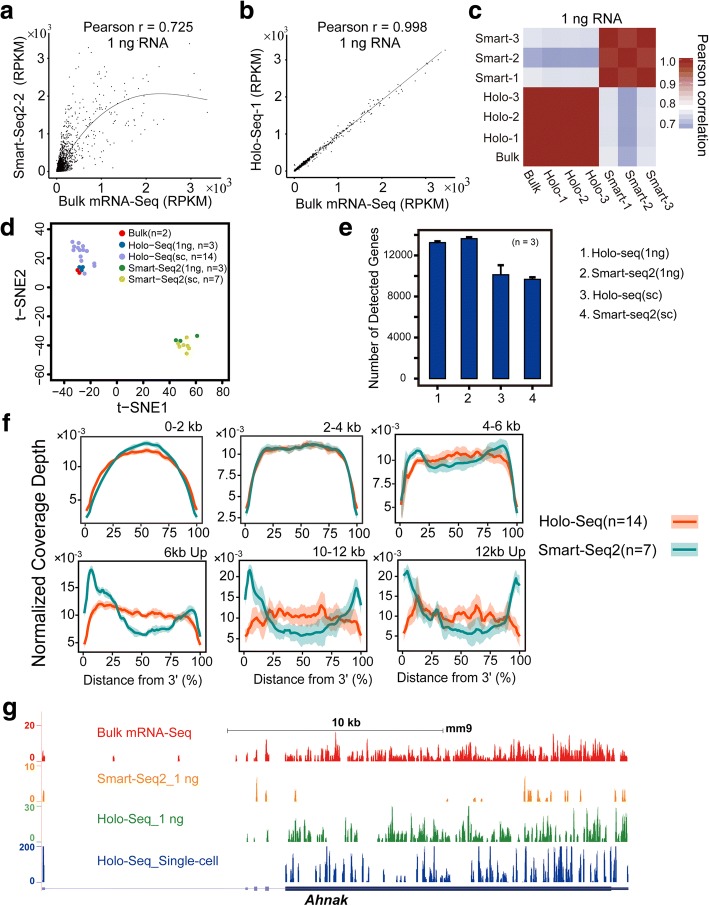
Fig. 1.
Holo-Seq profiles mRNA with the same accuracy and coverage as bulk mRNA-Seq. a An RPKM scatterplot of expressed genes between Smart-Seq2 and bulk mRNA-Seq. 1 ng of mESC total RNA was used. b An RPKM scatterplot of expressed genes between Holo-Seq (mRNA) and bulk mRNA-Seq. 1 ng of mESC total RNA was used. c Pearson correlation coefficient heat map of the mRNA profiles generated from 1 ng of total RNA by Holo-Seq (mRNA), Smart-Seq2, and bulk-mRNA-Seq. Three biological replicates were performed. d t-SNE analysis of mESCs (bulk-mRNA-Seq), mESC single cells (Holo-Seq and Smart-Seq2), and 1 ng mESCs total RNA (Holo-Seq and Smart-Seq2). Principal components were used as inputs. e Comparison of the number of genes detected by Holo-Seq and Smart-Seq2 from 1 ng mESC total RNA and mESC single cells at same mapped depths (6.8 M and 3.2 M). f Comparison of the read coverage across transcripts of different lengths between Holo-Seq and Smart-Seq2 from mESCs single cells. The read coverage over the transcripts is displayed along with the percentage of the distance from their 3′ end. Shaded regions indicate the standard deviation (SD). g The plot of the signals of Ahnak detected from mESCs (bulk mRNA-Seq), 1 ng mESC total RNA (Holo-Seq and Smart-Seq2), and a mESCs single cell (Holo-Seq) on the University of California Santa Clara (UCSC) gene browser