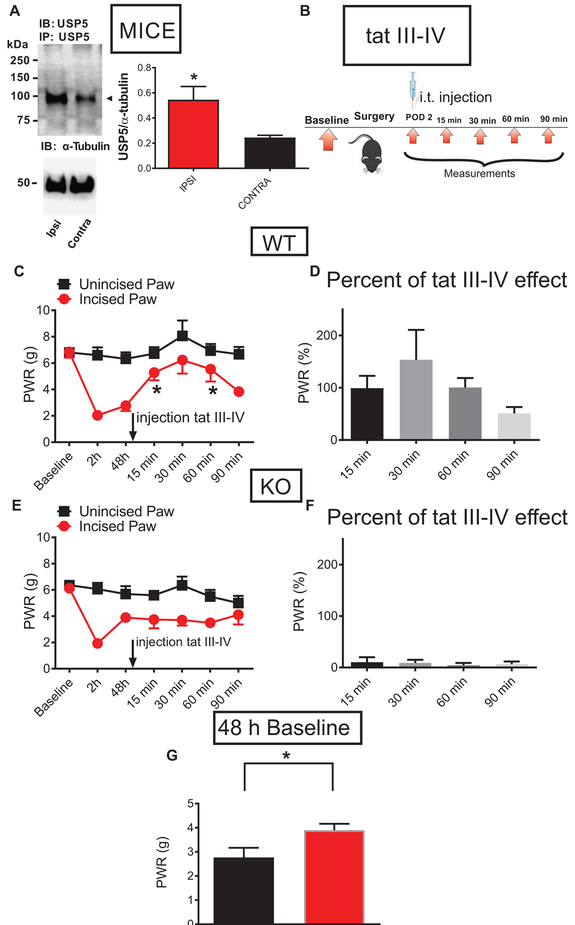
Fig. 5. Selective targeting of deubiquitination of Cav3.2 channels in nociceptors prevents the development of mechanical hypersensitivity in mice after plantar skin incision.
A. Representative Western blotting of three independent experiments of immunoprecipitated USP5 from DRG homogenates from ipsilateral and contralateral L4-L6 DRGs from WT mice post-incision, and a bar graph of the relative expression levels of USP5 48 h post-incision; n=3 animals: tissue homogenates of L4- L6 DRGs were harvested separately from ipsi and contralateral side of the spinal column and WB was performed in three animals, *P<0.05, Unpaired t-test; p=0.047. B. A time-course of in vivo experiment: 48 h post-surgery, WT and Cav3.2 KO mice were injected i.t. with tat III-IV peptide and PWRs were measured 15, 30, 60 and 90 minutes post-injection. C. The antihyperalgesic effect of injected tat III-IV peptide on PWR thresholds of incised paws in WT mice as measured 15, 30, 60 and 90 minutes post-injection. n=6 animals per group, *P<0.05, RM One-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post-hoc test; p=0.040. D. Robust antihyperalgesic effect of injected tat III-IV peptide on incised paws in WT mice was normalized to the pre-injection baseline (the same data as in panel C of this figure). E. Injected tat III-IV peptide did not significantly alter the PWR in incised paws of the Cav3.2 KO animals; n=6 animals per group, RM One-way ANOVA; p=0.754. F. The lack of effect of injected tat III-IV peptide on PWR thresholds of incised paws in Cav3.2 KO mice was normalized to the pre-injection baseline (the same data as in panel E of this figure). G. The difference between mechanical sensitivity thresholds recorded 48 h post-incision in WT (black bar) and Cav3.2 KO (red bar) mice; *P<0.05, n=6 animals per group, Unpaired t-test, p=0.04.