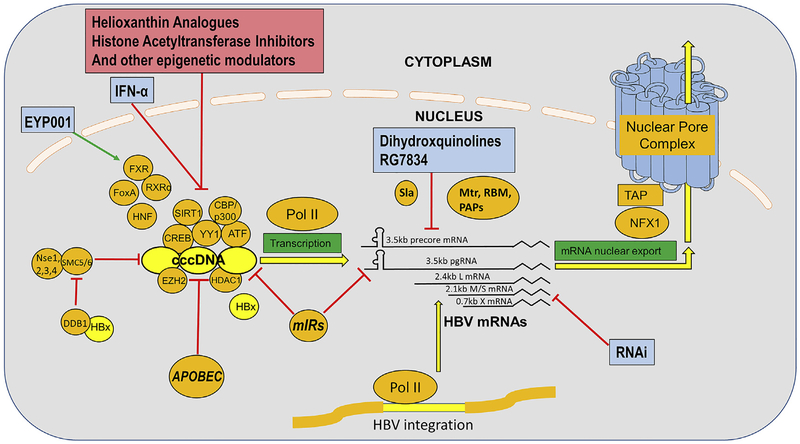
Fig. 4. Transcription of cccDNA and transport of viral RNA out of the nucleus.
HBV cccDNA is associated with, and presumably regulated by numerous host transcriptional factors, and unmodified and modified histones. Host SMC5/6 complex is shown, in this illustration, “attacking” (and transcriptionally repressing) HBV cccDNA, with HBx binding host protein DBB1 which, causes the degradation of SMC5/6, and thus promotes HBV cccDNA transcription. Host pol II transcribes HBV cccDNA as well as HBV DNA integrated in to the host chromosomes, and these transcripts are processed and transported out of the nucleus using numerous host functions, including polyadenylation, although the precise pathways of processing are not well established. Cellular functions mediating these steps are indicated in orange, research phase compounds that interfere with these steps are shown in pinkish red, with compounds that are clinical phase, or approved, in light blue. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)