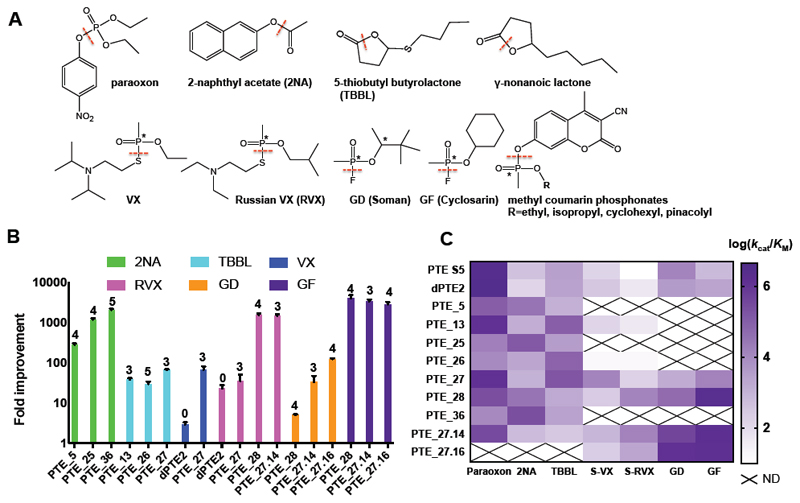
Figure 2. A designed repertoire of phosphotriesterases exhibits orders of magnitude improvement in a range of promiscuous activities, including the hydrolysis of highly toxic nerve agents.
(A) The bacterial PTE is a paraoxonase exhibiting additional promiscuous hydrolase activities. The dashed red lines indicate the bonds that PTE hydrolyses in each of the substrates tested in this study, and the asterisks indicate chiral centers. (B) Fold improvement in catalytic efficiency (kcat/KM) of the top FuncLib designs relative to PTE-S5, showing remarkable >1,000-fold improvement in nerve-agent hydrolysis efficiency in several designs. The number of active-site mutations is indicated above the bars. (C) Activity profiles of the top PTE designs. Several designs, most prominently PTE_27, PTE_28, and PTE_27.14, exhibit substantially broadened substrate selectivity relative to PTE S5. Data for nerve agents are shown for the more toxic Sp stereoisomers. Data are represented as mean ± standard deviations of duplicate measurements. N.D. - not determined. See also Tables S1-S3.