Figure 5. Advanced in vivo applications of metabolomics.
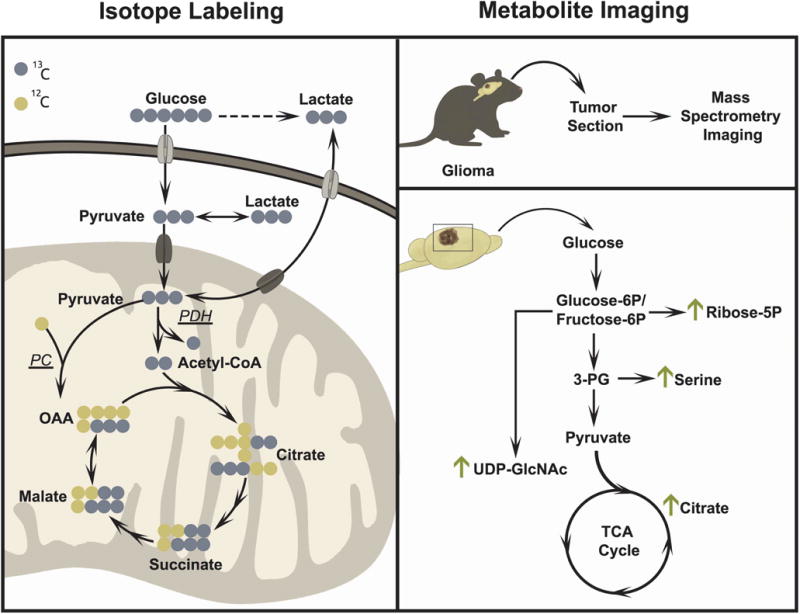
Isotope tracing (left) and metabolite imaging (right) are two examples of advanced applications of metabolomics. Isotope tracing studies in lung cancer patients have established that glucose and lactate are oxidized in the TCA cycle in vivo. These studies have also revealed the activity of both pyruvate dehydrogenase and pyruvate carboxylase (PDH and PC) in vivo. In the illustration, PDH activity results in TCA cycle intermediates with two 13C nuclei and PC activity results in TCA cycle intermediates with three 13C nuclei. Metabolite imaging (right) using matrix assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI) provides temporal and spatial resolution of metabolite abundance to observe metabolic differences across tissue sections. Metabolite imaging has been used in murine glioma models to assess changes in glycolytic and TCA cycle intermediates.
