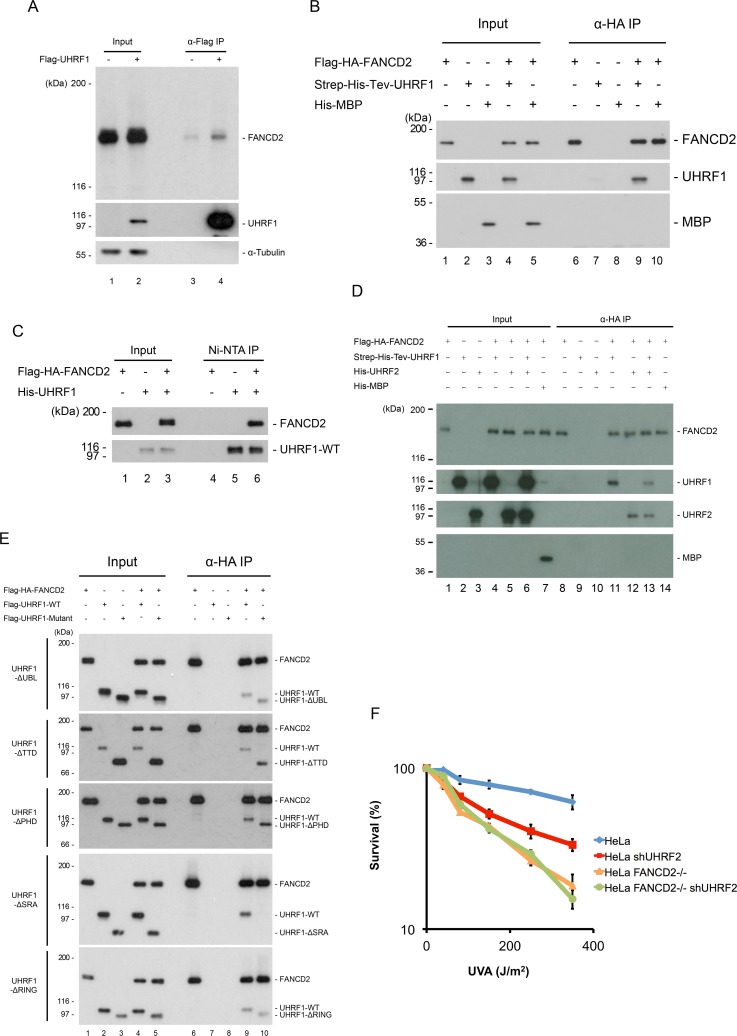
Fig 6. UHRF1 interacts directly with FANCD2.
A) Immunoprecipitation of Flag-UHRF1 from HeLa.shUHRF1 cells expressing exogenous Flag-UHRF1. HeLa.Scramble was used as a negative control. Cells were treated with TMP/UVA and allowed to recover for 1 hour before lysis, immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting. B) In vitro binding assay using Flag-HA-FANCD2, Strep-6xHis-Tev-UHRF1 (both purified from Sf9 cells) and 6xHis-MBP (purified from E. coli). HA-FANCD2 was immunoprecipitated and immunoblotting demonstrated co-immunoprecipitation of UHRF1 but not of MBP, which was used as a negative control. C) In vitro binding assay using Flag-HA-FANCD2 and 6xHis-UHRF1 (both purified from Sf9 cells). 6xHis-UHRF1 was purified using NTA-agarose, and immunoblotting demonstrated co-purification of FANCD2. D) In vitro binding assay using HA-FANCD2, Strep-6xHis-Tev-UHRF1, 6xHis-UHRF2 (all purified from Sf9 cells) and 6xHis-MBP (purified from E. coli). HA-FANCD2 was immunoprecipitated and immunoblotting demonstrated co-immunoprecipitation of UHRF1 and UHRF2 but not of MBP, which was used as a negative control. E) In vitro binding assays of Flag-HA-FANCD2 and wild type or deletion mutants of Flag-UHRF1 (purified from Sf9 cells). HA-FANCD2 was immunoprecipitated and immunoblotting demonstrated that the SRA domain of UHRF1 is responsible for the protein-protein interaction between UHRF1 and FANCD2. F) Clonogenic survival assay of HeLa, HeLa FANCD2 -/-, HeLa shUHRF2, and HeLa FANCD2 -/- shUHRF1 cells in response to TMP/UVA. Experiment was performed once in triplicate.