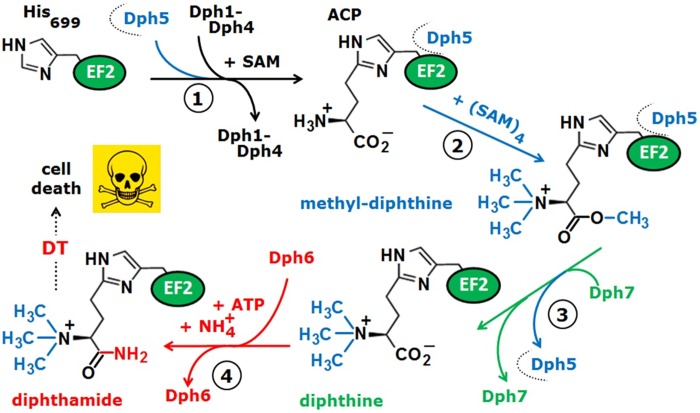
Fig 1. Diphthamide synthesis on yeast EF2 involves a multi-step pathway.
In step one (1, black label), Dph1-Dph4 use SAM as amino-carboxyl-propyl (ACP) donor to modify His-699 in EF2 with ACP. Next (2, blue label), Dph5 generates methyl-diphthine using the methyl donor function of SAM. Subsequently (3, green label), this intermediate is converted to diphthine by demethylase Dph7 before finally (4, red label), Dph6 generates diphthamide from diphthine using ammonium and ATP. Diphthamide can be ADP-ribosylated by diphtheria toxin (DT) to inactivate EF2 and cause cell death. Note that prior to ACP formation, Dph5 binds to unmodified EF2 and dissociates from intermediate methyl-diphthine in a fashion licensed by Dph7 [19,50]. The model is derived and up-dated from Schaffrath et al. (2014) [11].