Fig 5. Assessing the oncogenic potential of the K171E mutation in IKKβ on the IL-6 -dependent INA-6 cell line.
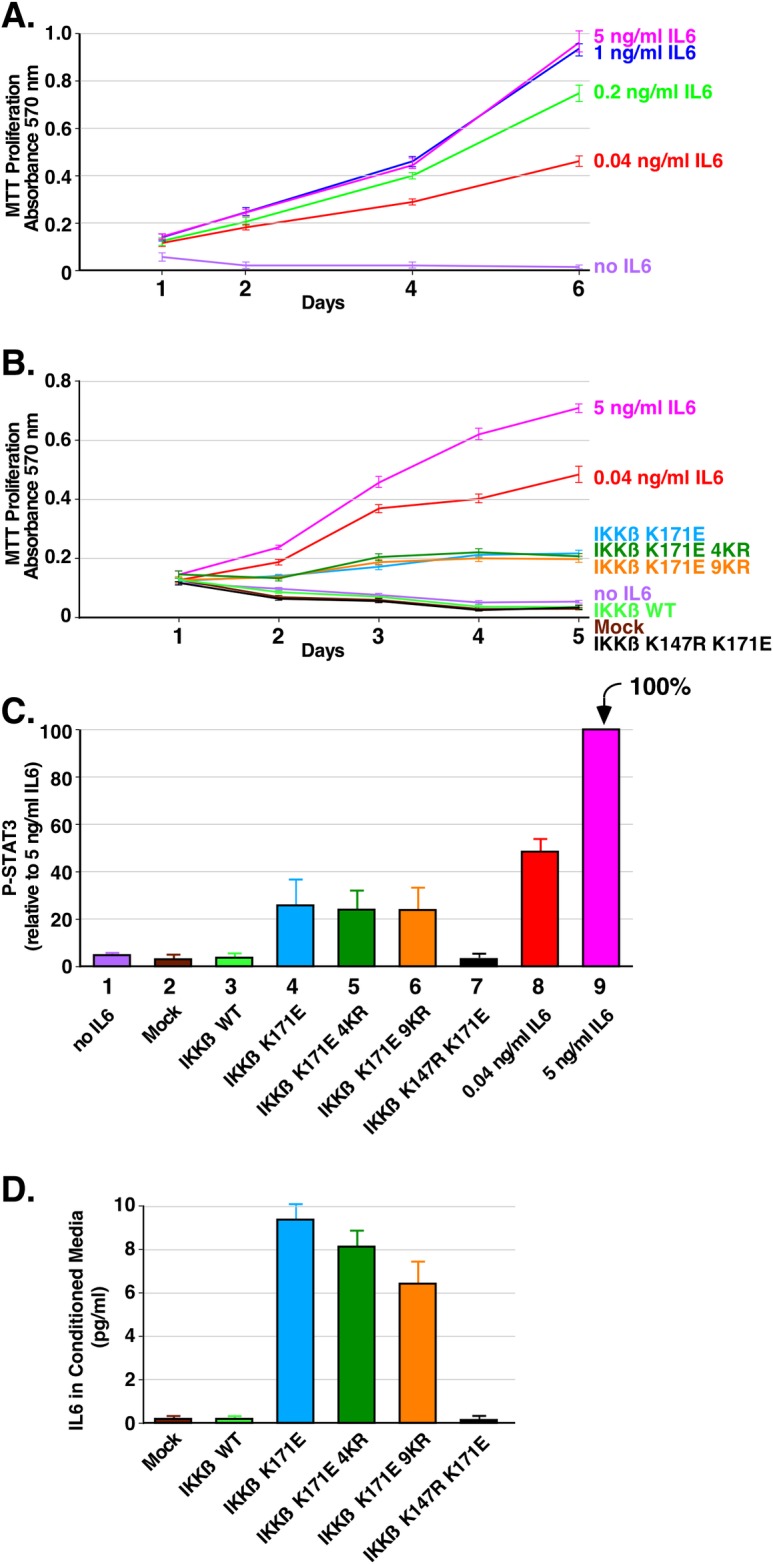
The human myeloma cell line INA-6 is completely dependent on exogenous IL-6 for growth and proliferation. (A) IL-6 concentration dependence of the INA-6 cells. Triplicate cultures of cells were grown in RPMI 1640 with 10% FBS and various concentrations of IL-6 (5, 1, 0.2, 0.04 and 0 ng/ml). Duplicate samples were collected at 1, 2, 4 and 6 days and assayed by MTT metabolic assay indicating the number of viable cells. Error bars show the standard deviation (B) Proliferation of INA-6 cells treated with conditioned media. Triplicate cultures of INA-6 cells were incubated in media collected from HEK293T cells expressing IKKβ derivatives. 10% FBS was added to the starvation media. Duplicate samples were collected at 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 days and assayed by MTT metabolic assay. Control samples were treated 5, 0.04 and 0 ng/ml of IL-6 as indicated. Error bars show the standard deviation (C) STAT3 activation induced by conditioned media from cells expressing IKKβ mutants. INA-6 cells were incubated as in B. for 48 h. Cells were lysed and immunoblotted for P-STAT3. Triplicate immunoblots were quantitated with 5 ng/ml of IL-6 set at 100%. Error bars show the standard deviation. (D). Detection of IL-6 in conditioned media from cells expressing IKKβ mutants. Using a sensitive ELISA kit for IL-6, the conditioned media was assayed in triplicate from each of two independent experiments. Concentrations were determined from a standard curve of IL-6.
