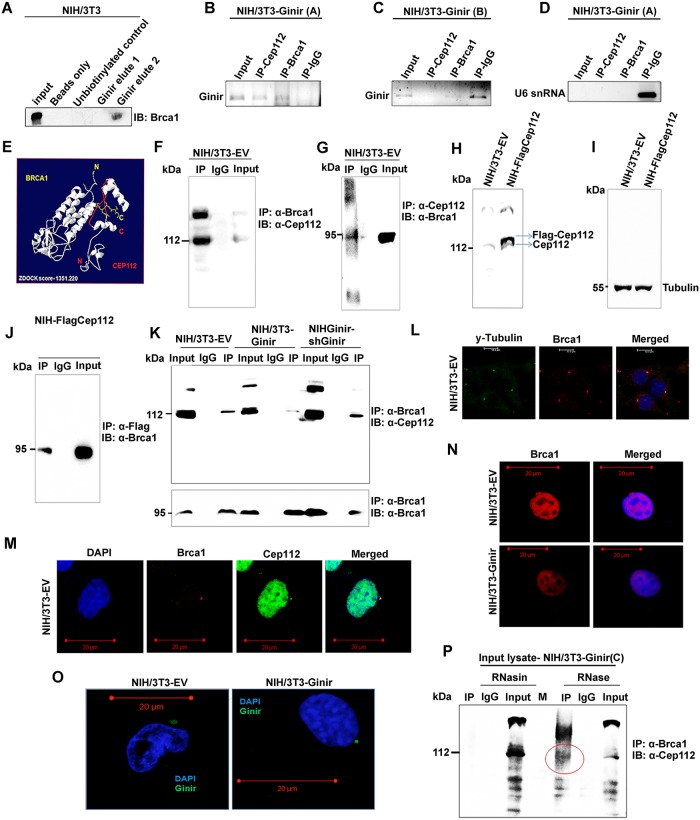
Fig 10. Ginir RNA impairs interaction between Cep112 and Brca1 proteins leading to genomic instability.
(A) RNA pull-down with biotinylated Ginir RNA in NIH/3T3 cells followed by western blotting with Brca1 antibody (sc-646, Santa Cruz). Pull-down with unbiotinylated RNA probe served as control for nonspecific binding. (B-D) RIP performed using both Cep112 and Brca1 antibodies followed by RNA isolation and RT-PCR with Ginir specific primers (G2F-G2R) in NIH/3T3-GinirA (B) and NIH/3T3-GinirB (C) cells. RIP assay was also followed by RT-PCR using nonspecific primers for U6 snRNA (D). Anti-IgG IP served as control for nonspecific interaction. (E) In silico model of Cep112 and Brca1 interaction generated through computational docking using ZDOCK tool. (F and G) Co-IP of Cep112 and Brca1 proteins in NIH/3T3-EV cells. IP was performed with Brca1 antibody (sc-646, Santa Cruz) followed by immunoblotting with Cep112 antibody (sc-246162, Santa Cruz) (F) and vice versa (G). Anti-IgG IP served as a control for nonspecific binding to the antibody. (H and I) Western blotting with Cep112 antibody (24928-1-AP, Proteintech) for validation of Flag-Cep112 overexpression in NIH/3T3 cells (H). Fifty μg of whole-cell protein lysates from each of the mentioned cell lines was loaded on 7% SDS-PAGE. Tubulin served as internal loading control (I). (J) Co-IP of Brca1 and Flag-Cep112 in NIH-Flag-Cep112 cells. IP was performed with Flag1 antibody followed by immunoblotting with Brca1 antibody (20649-1-AP, Proteintech). Anti-IgG IP served as a control for nonspecific binding to the antibody. (K) Co-IP of Brca1 and Cep112 proteins in NIH/3T3-EV, NIH/3T3-Ginir, and NIH-Ginir-shGinir2 cells. IP was performed with Brca1 antibody (sc-646, Santa Cruz) followed by immunoblotting with Cep112 antibody (24928-1-AP, Proteintech). Anti-IgG IP served as a control for nonspecific binding to the antibody. (L) Confocal images showing colocalisation of Brca1 with γ-tubulin in NIH/3T3-EV cell line. Nuclei were stained with DAPI. Scale bars, 10 μm. (M) Confocal images showing colocalisation of Brca1 protein with Cep112 protein in NIH/3T3-EV cell line. Nuclei were stained with DAPI. Scale bars, 20 μm. (N) Confocal imaging for Brca1 expression in NIH/3T3-EV and NIH/3T3-Ginir cells. Scale bars, 20 μm. (O) RNA-FISH using Ginir-specific probe (probe 1, FAM labelled) in NIH/3T3-EV cells visualised by confocal imaging. Scale bars, 20 μm. (P) Co-IP of Brca1 and Cep112 in NIH/3T3-Ginir(C) cells wherein lysates were treated independently with RNase (A, H, and III mix) or RNasin. Both RNase- and RNasin-treated lysates were immunoprecipitated with Brca1 antibody (sc-646, Santa Cruz) and blotted using Cep112 antibody (sc-246163, Santa Cruz). IP with anti-IgG served as control. Brca1, breast cancer type 1 susceptibility protein; Cep112, centrosomal protein 112; FAM, fluorescein amidite; Ginir, Genomic Instability Inducing RNA; IgG, immunoglobulin G; IP, immunoprecipitation; RIP, RNA-immunoprecipitation; RNasin, RNase inhibitor; RT-PCR, reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction; snRNA, small nuclear RNA.