Figure 1.
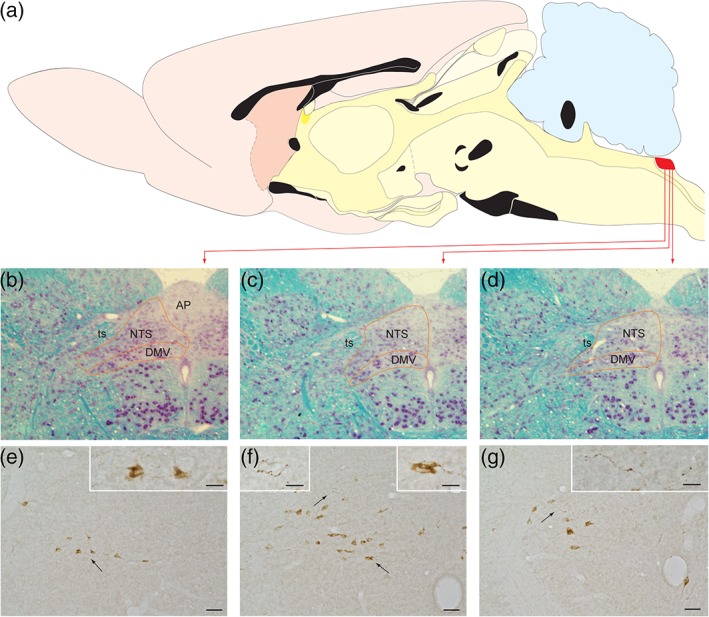
The portion of the caudal nucleus of the solitary tract (cNTS) within which GLP‐1 neurons are sequestered is illustrated for the rat brain. (a) The location of the cNTS within the hindbrain dorsal motor vagal complex is marked in red. (b–d) The cytoarchitecture of this cNTS region is depicted in three coronal sections stained with the Kluver–Barrera method. (e–g) Immunoperoxidase labeling reveals GLP‐1+ profiles in coronal sections through rostrocaudal levels comparable to those shown in panels (b–d). Arrows indicate specific regions shown at higher magnification in the panel insets. Scale bars: 50 μm in (e–g), and 20 μm for the insets within those panels. AP = area postrema; DMV = dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus; NTS = nucleus of the solitary tract; ts = solitary tract [Color figure can be viewed at http://wileyonlinelibrary.com]
