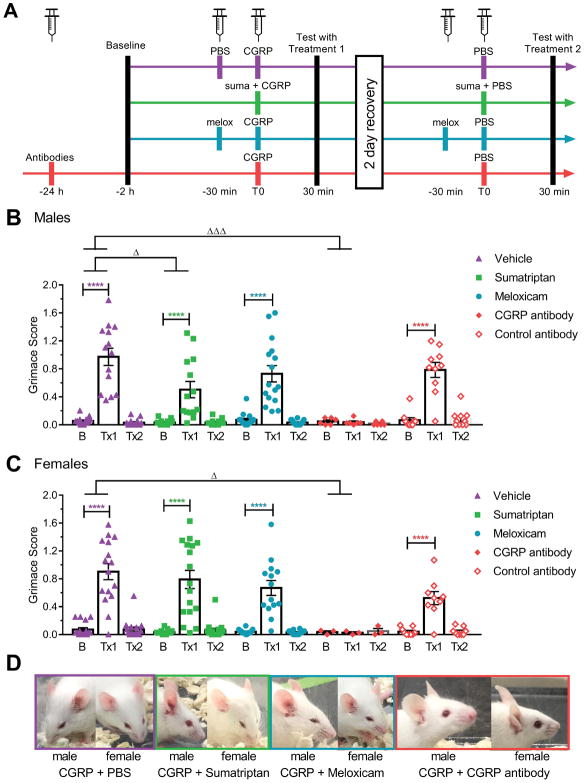
Figure 2. Effect of treatments on CGRP-induced spontaneous grimace.
(A) Experimental design. (B, C) MGS scores of male (B) and female (C) CD1 mice at baseline (B) and after treatments 1 and 2 (Tx1 and Tx2). Mice were pretreated with isotype controls or CGRP monoclonal antibody ALD405 (30 mg/kg IP) 24 hours prior to testing, with meloxicam (2 mg/kg IP) 60 minutes prior to testing, or with vehicle (PBS, 10 ml/kg IP) or sumatriptan (0.6 mg/kg IP) 30 minutes prior to testing. For Tx1, all mice received CGRP (0.1 mg/kg IP) 30 minutes before testing. For Tx2, all mice received vehicle (PBS) 30 minutes before testing. The mean grimace scores were measured 30 minutes after the last injection. (D) Representative pictures of a male and a female taken during the assay 30 minutes after the last injection for the CGRP + PBS group (purple), CGRP + sumatriptan group (green), CGRP + meloxicam group (blue), CGRP + CGRP antibody (red). Average between 3 experiments scored by two blinded individuals (n=20 to 30 per group, ± SEM). Two-way repeated measures ANOVA P < 0.0001 for treatment factor, Dunnett’s multiple comparison test to compare treatment 1 to baseline, ****P < 0.0001. For comparisons across treatment groups involving different animals, differences of changes from baseline were compared across treatment groups. Deltas (score at treatment time – score at baseline) were compared across treatment groups using a one-way ANOVA (with factor treatment), followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparison test, ΔP < 0.05, ΔΔΔP < 0.001.