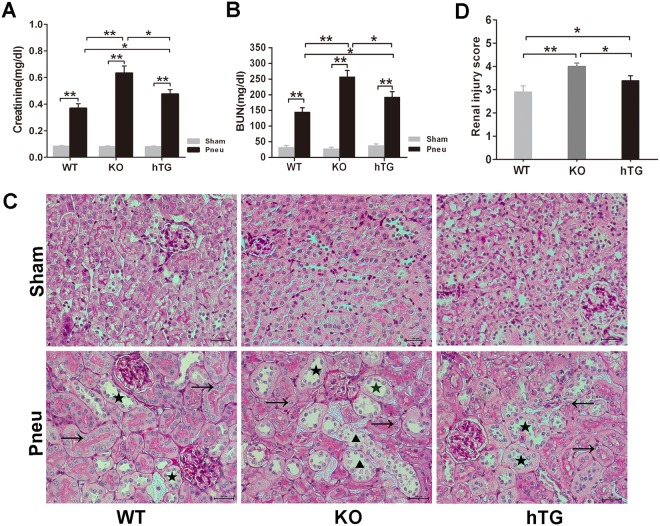
Figure 5.
Effects of pulmonary and/or renal SP-D on bacterial pneumonia-induced AKI. The infected mice exhibited AKI by a significant elevation of Scr (A) and BUN (B). The infected hTG mice had significantly higher Scr and BUN than infected WT mice and lower Scr and BUN than infected KO mice. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, One-way ANOVA, Newman-Keuls multiple comparison post hoc test (n = 6/group). (C) Renal histology from PAS staining showed normal kidney architecture in all sham groups of mice, suggesting that SP-D deficiency in the kidney did not affect kidney development and formation of normal kidney structure. Bacterial pneumonia-induced AKI were characterized by the presence of vacuolar degeneration of tubular cells (arrows), brush border loss with tubular lumen dilatation (stars) and cast formation (triangles). Magnification 200×. Scale bars = 100 μm. (D) Semi-quantitative analysis demonstrated that renal injury score was significantly higher in infected KO mice compared to infected WT and hTG mice. Furthermore, when compared to infected WT mice, hTG mice had significantly higher renal injury score. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, t test (n = 6/group). Sham = Sham infection, Pneu = Pneumonia.