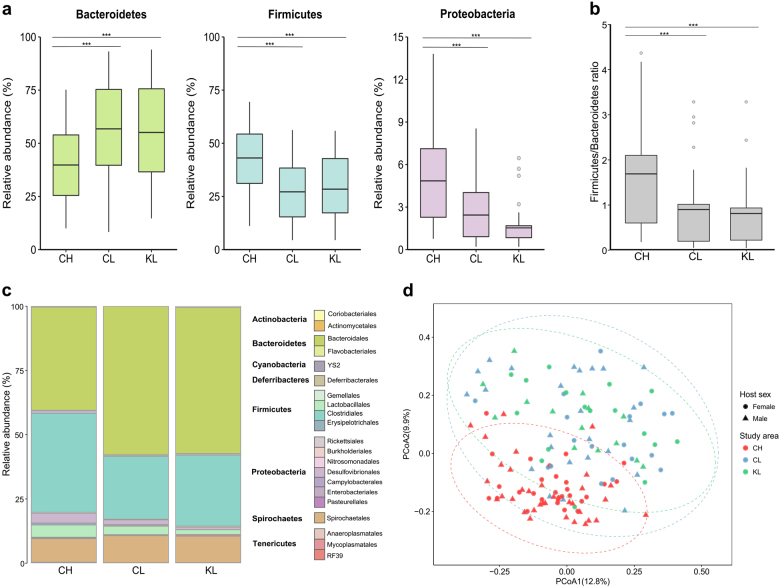
Fig. 1.
Radiation-associated differences in bank vole gut microbiota community composition and beta diversity. a Relative abundances of three major bacterial phyla and b Firmicutes to Bacteroidetes ratio (F:B) in the gut microbiota of bank voles inhabiting areas that differ in levels of environmental radiation. Asterisks indicate significant differences among areas contaminated (CH) and uncontaminated (CL) with radionuclides within the Chernobyl Exclusion Zone and an uncontaminated area near Kyiv (KL), Ukraine (Bonferroni-corrected Kruskal–Wallis test). ***P < 0.001. c Mean relative abundance of bacterial taxa at order level in the bank vole gut microbiota. Unassigned taxa (<2.3%) are not shown. d PCoA on Bray–Curtis dissimilarity distances between bank vole gut microbiota profiles among the three study areas. Each point represents a single sample, shape indicates host sex, colored according to study area: CH, red (n = 63); CL, blue (n = 43); KL, green (n = 31). Ellipses represent a 95% CI around the cluster centroid. Clustering significance by treatment group was determined by adonis, P < 0.001