Fig. 6.
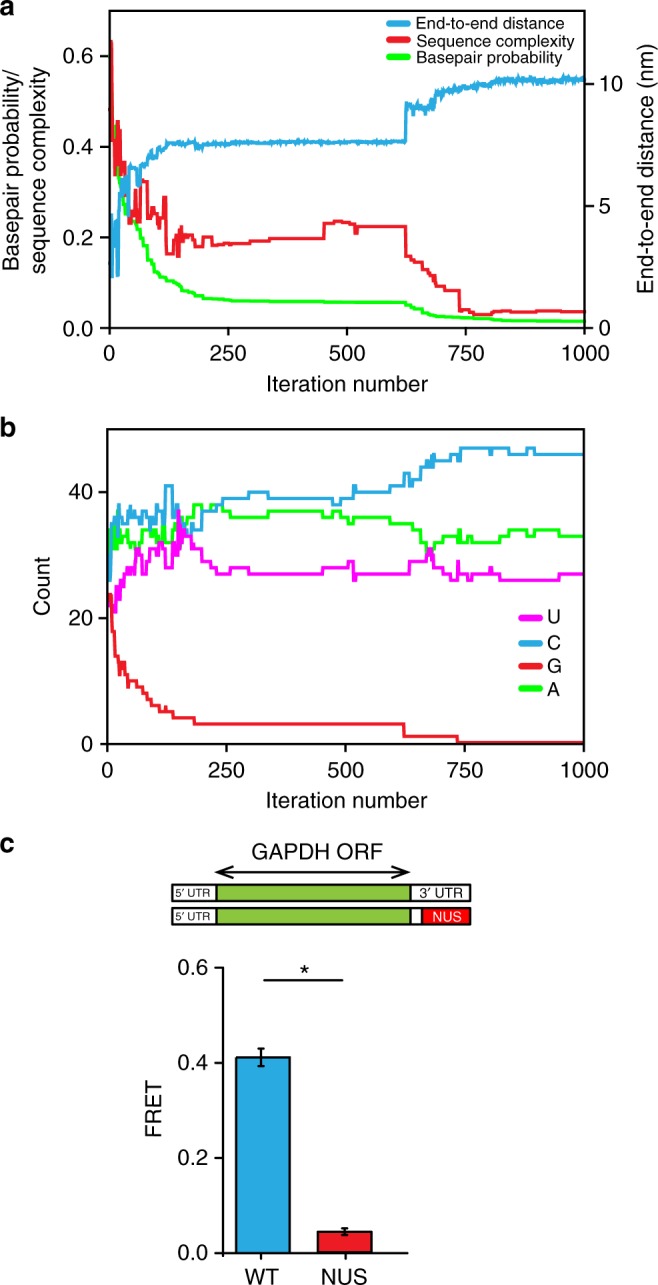
Manipulation of end-to-end distances in GAPDH mRNAs in silico with a genetic algorithm. 106 nucleotides in the 3′ end of the 3′ UTR in GAPDH mRNA are computationally evolved in silico by a genetic algorithm. a End-to-end distance (blue), sequence complexity (red), and base pair probability (green) as functions of iteration number are shown for a single in silico sequence evolution experiment. b Evolution of nucleotide composition in the sequence evolution in silico experiment shown in a. Frequency of adenosine (A), cytidine (C), guanosine (G), and uridine (U) are shown in magenta, blue, red, and green, respectively. c FRET values were measured in wild-type GAPDH mRNA (blue) and the GAPDH mRNA variant with the non-repetitive unstructured (NUS) 106 nucleotide sequence in the 3′ end of the 3′ UTR (red) designed by a genetic algorithm. Each FRET value represents the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. A star indicates that FRET values are different, as p-values determined by the Student t-test were below 0.05
