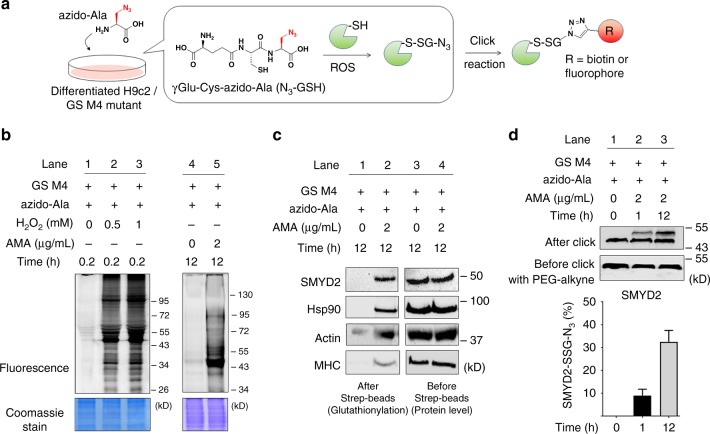
Fig. 1.
SMYD2 is glutathionylated in response to ROS. a A scheme for a clickable glutathione approach: a glutathione synthetase mutant (GS M4), which synthesizes azido-glutathione (γGlu-Cys-azido-Ala, N3-GSH), was expressed in differentiated H9c2 cells. After incubation of azido-Ala, cells were subjected to ROS. Glutathionylated proteins in lysates were identified after click reaction. b In-gel fluorescence detection of glutathionylated proteins. H9c2 cells expressing GS M4 were incubated with azido-Ala (0.6 mM) for 20 h and treated with H2O2 or antimycin A (AMA). Collected lysates were then subjected to click reaction with rhodamine-alkyne for fluorescence detection. c Identification of individual glutathionylated proteins. Glutathionylated proteins were subjected to click reaction with biotin-alkyne and pull-downs with streptavidin-agarose, and detected by western blotting with individual antibodies, including SMYD2, Hsp90, actin, and myosin-heavy chain (MHC). d The level of glutathionylation on SMYD2. Lysates were subjected to click reaction with 2-kD PEG-alkyne. The mass shift of SMYD2 was analyzed by Western blotting. The level of glutathionylation on SMYD2 (SMYD2-SSG-N3) was calculated by dividing the amount of glutathionylated SMYD2 (upper band) by a total amount of SMYD2 (upper and bottom bands) in the blot after click reaction. Data represent the mean ± SD. All data are representative of 3 independent experiments