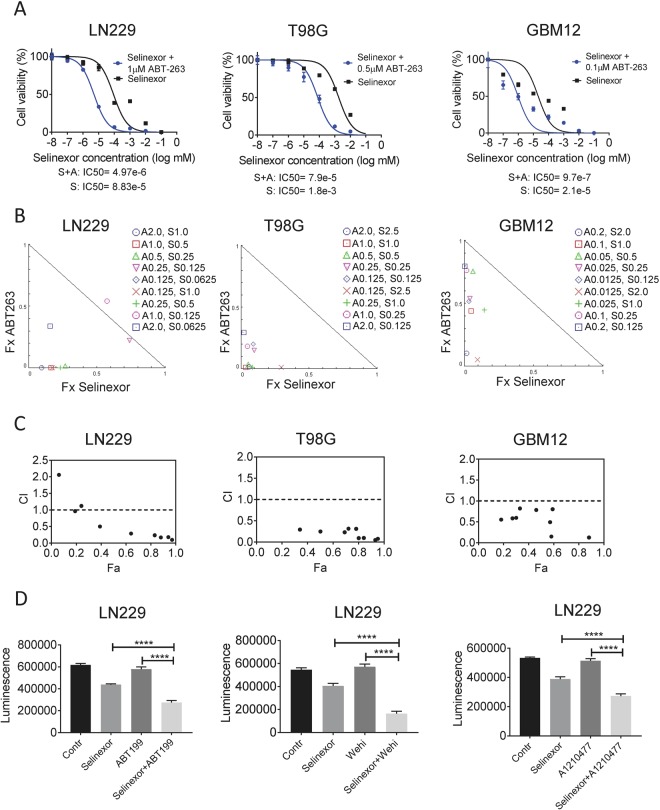
Figure 1.
The combination treatment of BH3-mimetics and selinexor synergistically reduce cellular proliferation of glioblastoma cells. (A) The indicated glioblastoma cell lines, LN229, T98G and GBM12 (patient-derived xenograft) cells, were treated with increasing concentrations of selinexor in the presence or absence of the BH3-mimetic, ABT263, at 1 μM. After 72 h, cell viability assays were performed and IC50 values were calculated, using non-linear regression. Shown are means and SD. (B) LN229, T98G or GBM12 (patient-derived xenograft) cells were treated with a range of concentrations of ABT263, selinexor or the combination. 72 h after treatment, cell viability assays were performed and synergism analysis was performed. Shown are the isobolograms for the three different cell lines. Points below the border line are considered synergistic, whereas points above are antagonistic. Points on the line are additive. (C) LN229, T98G and GBM12 (patient-derived xenograft) cells were treated as in B. Shown is the combination index (CI) vs. the fractional response rate (Fa). CI values smaller than 1.0 indicate a synergistic interaction. (D) LN229 GBM cells were treated with selective BH3-mimetics, ABT199 (Bcl-2 inhibitor), WEHI-539 (Bcl-xL inhibitor) or A1210477 (Mcl-1 inhibitor) in the presence or absence of selinexor. Contr: Control, Shown are means and SD of total luminescence values. *p < 0.05; **/***/****p < 0.01.