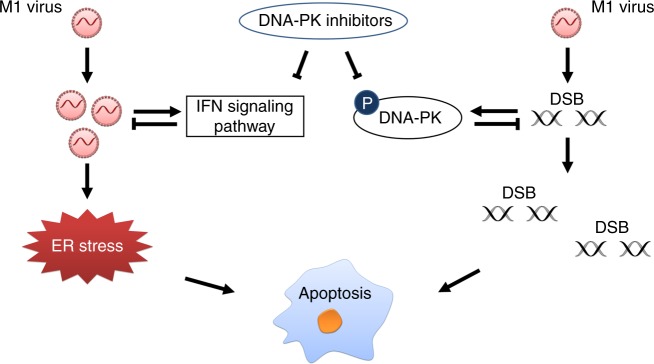
Fig. 8.
Graphical model of DNA-PKI and OV M1 combination therapy. A subset of tumour cells are innately resistant to oncolytic virus M1, and infection induces the production of type I IFN, which hampers viral replication. Treatment with DNA-PK inhibitors blocks the IFN antiviral response induced by M1 virus, resulting in increased virus replication, and triggers prolonged and severe ER stress. In addition, M1 virus causes DNA damage in tumour cells. In response to DNA damage, DDR pathways are immediately activated by PI3K-related kinases, including DNA-PK, to maintain gene stability. Thus, co-treatment with DNA-PK inhibitors hinder the DNA repair function and promote DNA damage induced by M1 virus. Above all, the DNA-PK inhibitors act synergistically with OV M1 by attenuating the IFN antiviral pathway and increasing DNA damage-mediated cell apoptosis