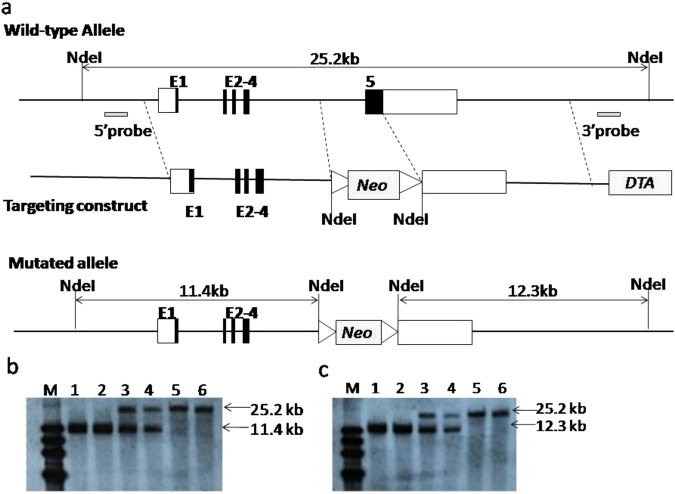
Figure 1.
Targeting vector construction strategies. (a) The top graph shows the wild-type allele with exon 1 to 5 in the murine iGb3S WT locus, together with relevant enzyme restriction sites and probes for Southern blot analysis. The middle graph shows the targeting vector constructed by replacing a 1.5-kb fragment encoding the iGb3S exon 5 with a loxP-flanked neomycin-resistance gene cassette (neo), and a diphtheria toxin A (DTA). The lower graph shows the mutated allele with an11.4 kb Nde1-fragment at the 5′-arm immediately upstream of the neo cassette and 12.3 kb of the Nde1-fragment at the 3′-arm immediately downstream of the neo cassette. Coding and non-coding regions of exon 1–5 are marked by filled and non-filled boxes, respectively. Homology arms are depicted as bold lines. (b,c) show Southern blotting results. (b) Genomic DNA was digested with NdeI in the 5′-probe and resulted in 25.2 kb and 11.4 kb fragments. (c) Genomic DNA was digested with NdeI in the 3′-probe and resulted in 25.2 kb and 12.3 kb fragments. M, DNA marker; lanes 1 and 2 are mut/mut, lanes 3 and 4 are mut/wt; lanes 5 and 6 are wt/wt.