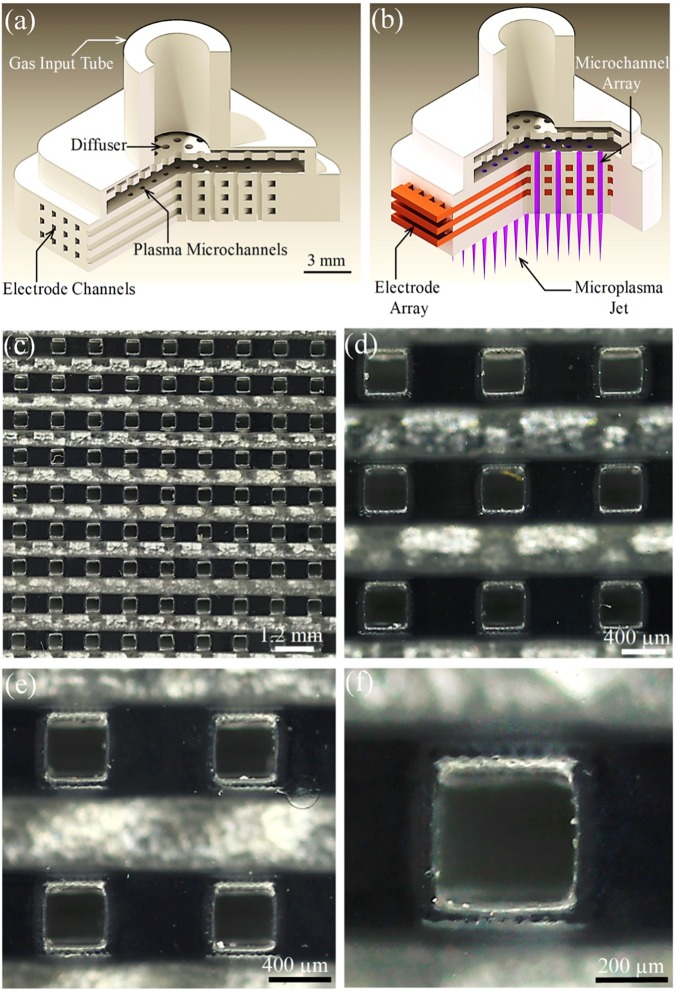
Fig. 1.
Diagrams (in cutaway view) of the 3D-printed microplasma jet array devices: a monolithic structure prior to the insertion of electrodes; b illustration of the installed electrode arrays (in red) and the array in operation, producing multiple plasma jets (in blue). Feedstock gas (He in the present experiments) is injected by means of the tube at top, and the applied electric field is oriented parallel to the direction of gas flow: (see through f); Optical micrographs of a 9 × 9 array of square cross-section microchannels, shown at increasing levels of magnification: c the full 9 × 9 array; d a 3 × 3 section of the full 81 microchannel array; e a 2 × 2 array segment (the lower of the two horizontal lines at the bottom of all four channels is a spurious optical reflection); f a single microchannel, showing the spatial resolution of the 3D printing process