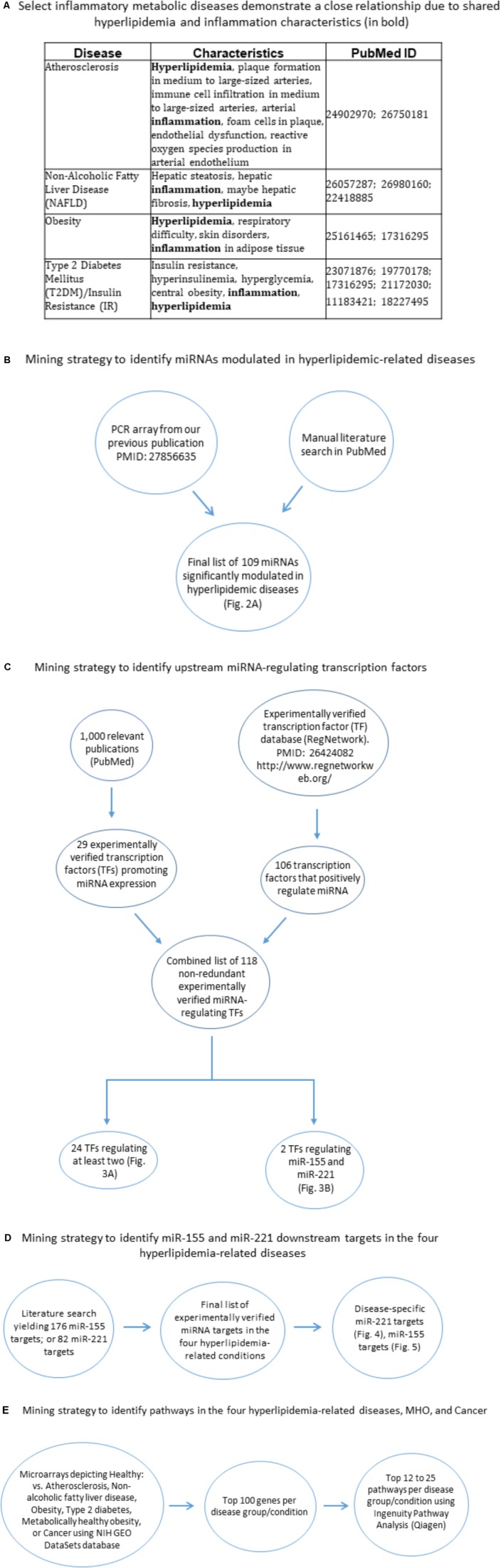
FIGURE 1.
Flow chart of database mining strategy. (A) Select inflammatory metabolic diseases demonstrate a close relationship due to shared hyperlipidemia and inflammation characteristics. (B) Two methods of data mining were employed: PCR array data from our lab (PMID: 27856635) and literature search. (C) Two methods of data mining were employed. The first was analyzing 1,000 papers using PubMed, narrowing down to 66 relevant publications, yielding 29 experimentally verified TFs. The second method involved the use of the RegNetwork database, yielding 106 experimentally verified transcription factors. In all, a total of 135 overlapping transcription factors were obtained. This combined list was then assessed using two approaches: (1) In each single disease and co-morbid diseases group, TFs that regulated at least two miRNAs were chosen as significant and then overlapped to define unique and shared TFs; (2) identified transcription factors that regulate miR-155 and miR-221. (D) Literature search for miR-155 targets and miR-221 targets, which were then assessed whether they played roles in any of the four hyperlipidemia-related diseases. (E) Using NIH GEO DataSets database, microarray comparing healthy vs. disease human subjects; metabolic unhealthy vs. metabolically healthy obese patients were obtained. The top 100 significantly upregulated genes per condition were obtained and then the top 12–25 pathways per condition were obtained. Finally, these pathways were overlapped to identify shared pathways (Figure 8). TF, transcription factor.