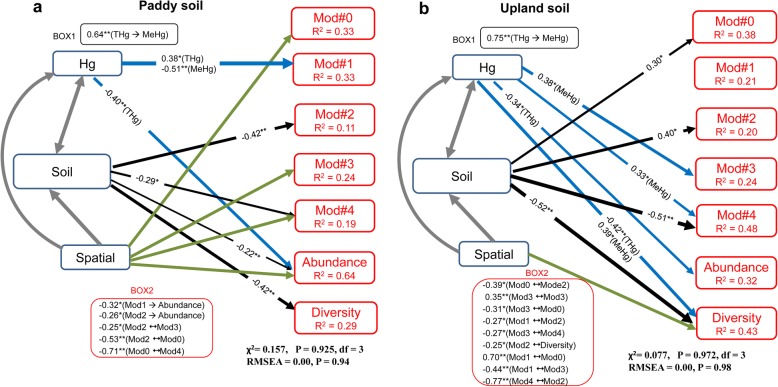
Fig. 4.
Mechanistic modeling identifying the direct and indirect effects of Hg on bacterial abundance, diversity, and the relative abundance of ecological clusters (modules, Mod) within co-occurrence networks in paddy (a) and upland (b) soils. The Hg box includes total Hg and methylmercury, and the spatial box includes longitude and latitude. The soil box includes soil properties that were represented by the three major components by performing principal component analysis of soil variables including pH, soil organic carbon (SOC), C: N, and others (Additional file 1: Table S3). The thickness of the arrow represents the strength of the relationship when significant, while no arrow is showed when the effect is not significant. Numbers adjacent to arrows are path coefficients with significant levels. R2 denotes the proportion of variance explained. Spatial (latitude and longitude) influence was included to control spatial autocorrelation; however, in this case, path coefficients were not included for simplicity. The BOX2 includes the significant correlations between modules, diversity, and abundance. The rest of significant effects are available in Additional file 1: Table S4 (P < 0.05).*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01