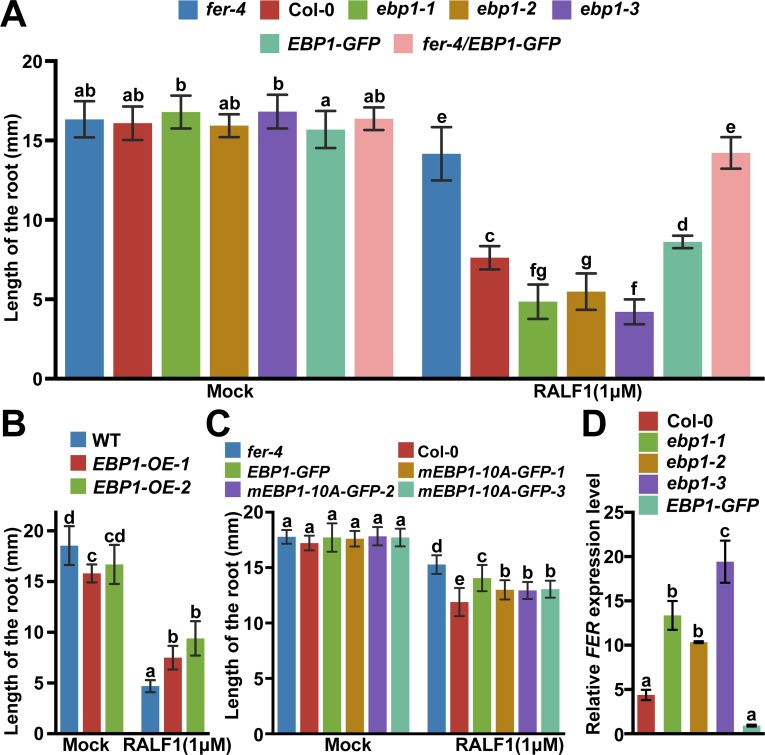
Fig 5. EBP1 inhibits the RALF1 peptide response.
(A) ebp1 mutants are hypersensitive, whereas fer-4, EBP1-GFP and fer-4/EBP1-GFP plants are less sensitive to RALF1 peptide in root growth assay as compared to the WT. n = 10. (B) EBP1-OE lines (rdr6 background) are less sensitive to RALF1 than the WT in root elongation assay. n = 10. (C) EBP1-GFP is less sensitive to RALF1 than Col-0, whereas mEBP1-10A-GFP lines show more sensitivity to RALF1 than EBP1-GFP but less sensitivity than Col-0. n = 9. Three independent lines of mEBP1-10A-GFP were gained respectively, and similar results were obtained. Root growth assays were performed in four independent experiments, and similar results were obtained. (D) FER mRNA levels in ebp1 mutants and EBP1-GFP lines. Quantification of FER mRNA levels relative to Actin was done using qRT-PCR. Data points are means +/− SD of two technical replicates. Values with different letters are significantly different (P < 0.05) from each other, tested by one-way ANOVA. Similar results were obtained in two independent experiments. Numerical data used to generate the plot are provided in S1 Data. EBP1, ErbB3-binding protein 1; EBP1-OE, EBP1-overexpression; qRT-PCR, quantitative reverse transcription PCR; RALF1, rapid alkalinization factor 1; WT, wild type.