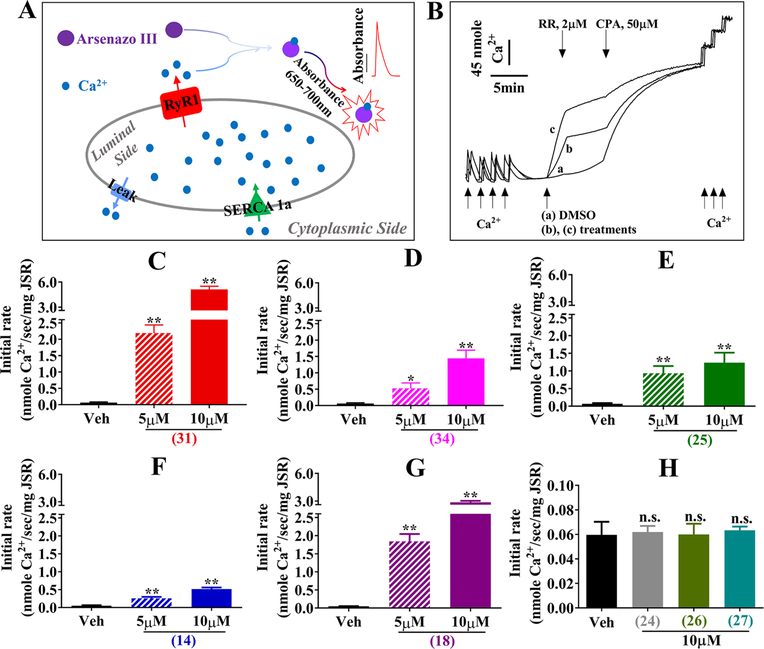
Figure 6.
Microsomal Ca2+ release triggered by selected HOCs of marine origin. (A) Schematic illustration showing the Ca2+ transport system monitored with Ca2+ dye Arsenozo III. (B) Representative traces of Ca2+ fluxes. Microsomal (JSR) vesicles were loaded with 4 sequential additions of 45 nmole CaCl2, 60−90 s after the final bolus of Ca2+ was accumulated into vesicles, vehicle (0.2% DMSO, a) or test compounds (b or c) was introduced into one of the cuvettes. Ruthenium red (RR, 2 μM), a RyR blocker, was then added to each cuvettes to confirm the engagement of RyR1 followed by addition of SERCA inhibitor, cyclopiazonic acid (CPA, 50 μM), and CaCl2 were added to calibrate absorbance unit into absolute Ca2+ in nmol. The Ca2+ release rate of initial 60 s upon the addition of Veh or test compounds (5 or 10 μM) are summarized in Panels C−H. Data shown are from 3 to 6 independent experiments using 2 different microsomal membrane preparations. Data expressed as Mean ± SD and one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test was performed using Graph Pad 7.03. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 vs Veh. And n.s. indicates no significant difference compared with Veh.