Figure 2:
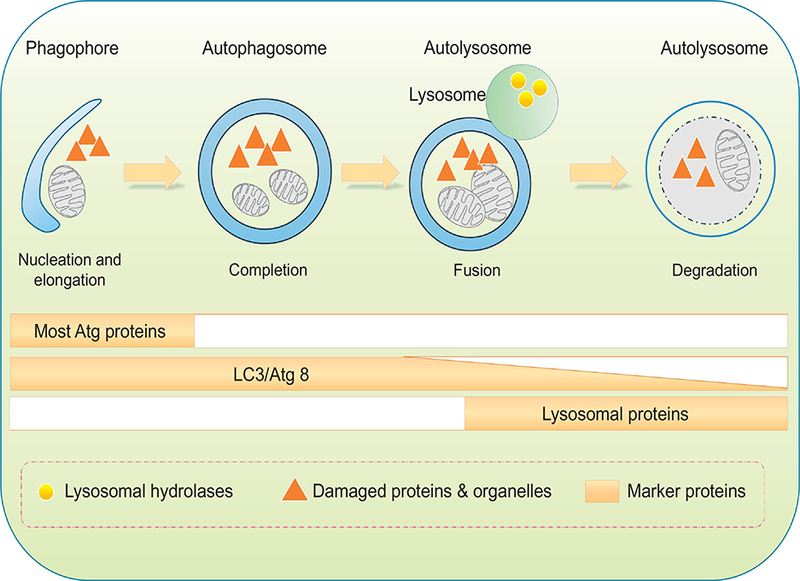
Schematic diagram of sequential autophagy events in a step-wise manner. Phagophore forms with initial sequestration of aged or damaged proteins and organelles; phagophores then undergo a series of further membrane expansion and elongation events to yie ld a completed double-membrane sequestering vesicle named autophagosome. During formation of autophagosome, various substrates (cytosolic proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, glycogen, damaged organelles, and invasive microbes, also known as cargo) of autophagy are encapsulated within the autophagosomal vesicle. Autophagosomes fuse with lysosomes to form autophagolysosmes, where cargos are digested by lysosomal hydrolases. Protein markers are identified throughout each individual steps. Most ATG proteins are visible during early stages of autophagy initiation while the elevated levels of lipidated LC3/Atg8 can sustain for a much longer period of time.
