Figure 4.
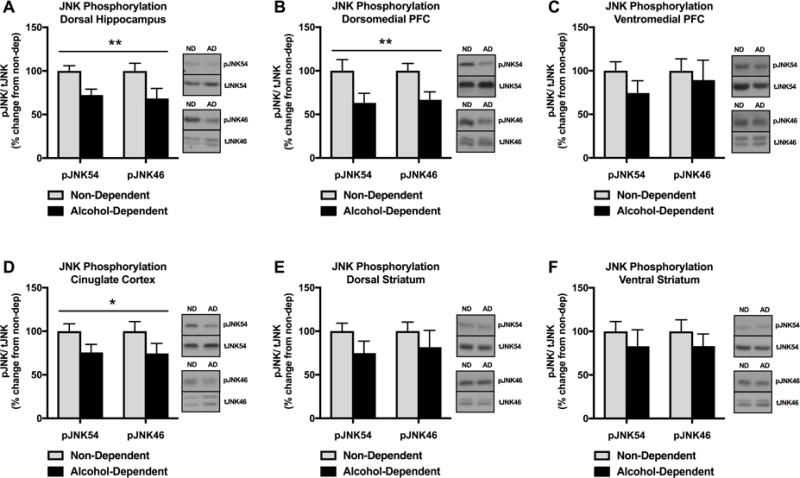
Effect of alcohol dependence and acute (8 h) withdrawal on JNK phosphorylation in in the HP, dmPFC, vmPFC, CC, DS, VS. (A) pJNK was significantly decreased in the HP of alcohol-dependent animals in withdrawal compared to non-dependent animals (**p<0.01). (B) pJNK was significantly decreased in the dmPFC of alcohol-dependent animals in withdrawal compared to non-dependent animals (**p<0.01). (C) There was no difference in pJNK in the vmPFC between alcohol-dependent animals in withdrawal and non-dependent animals (p>0.05). (D) pJNK was significantly decreased in the CC of alcohol-dependent animals in withdrawal compared to non-dependent animals (*p<0.05). (E) There was no difference in pJNK in the DS between alcohol-dependent animals in withdrawal and non-dependent animals (p>0.05). (F) There was no difference in pJNK in the VS between alcohol-dependent animals in withdrawal and non-dependent animals (p>0.05). Significant effects were observed in both p46 and p54 molecular weight bands representing JNK1-3 phosphoisoforms. Data are expressed as pJNK levels normalized to total JNK levels. Representative bands indicate changes in pJNK54 (single band), tJNK54 (single band), pJNK46 (single band), and tJNK46 (doublet).
