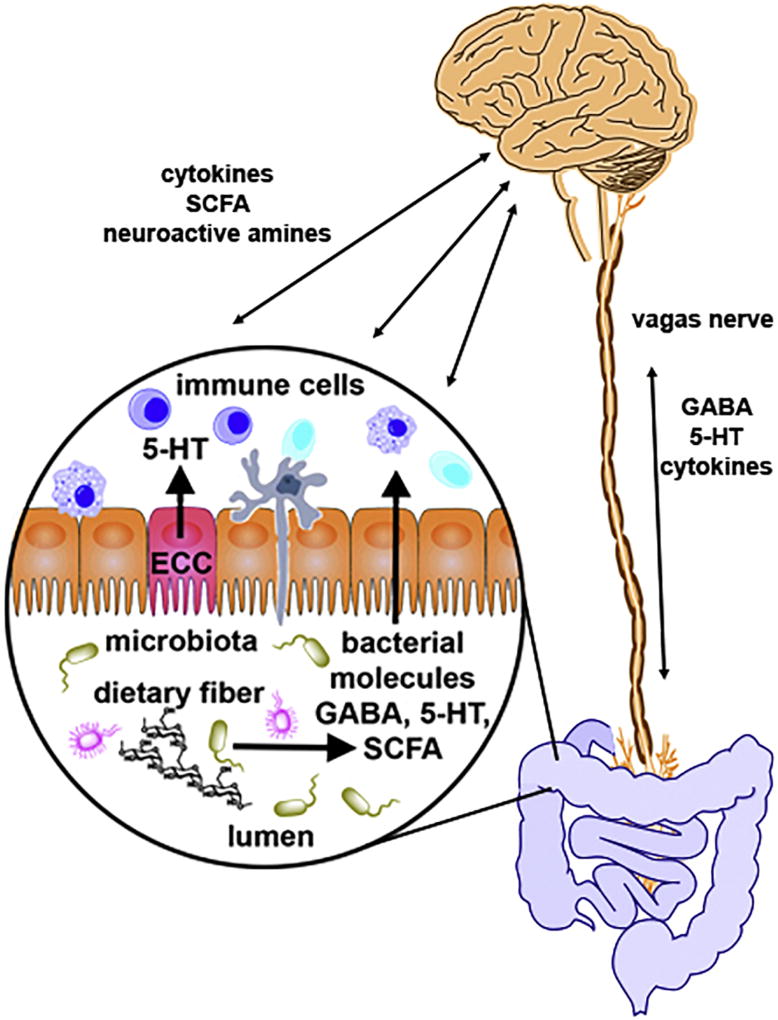
Figure 1. Representation of the bidirectional communication between the gut-microbiota-brain axis.
Signaling can occur directly via the vagus nerve, through signaling molecules such as GABA (γ-Aminobutyric acid), serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT) and antiinflammatory cytokines. Conversely, signaling can occur indirectly, through chemical messengers that are released into the periphery and act in an endocrine manner including GABA, 5-HT, produced by enterochromaffin cells (ECC) and short chain fatty acids (SCFA), such as butyrate and propionate, produced through bacterial fermentation of nondigestible fiber.