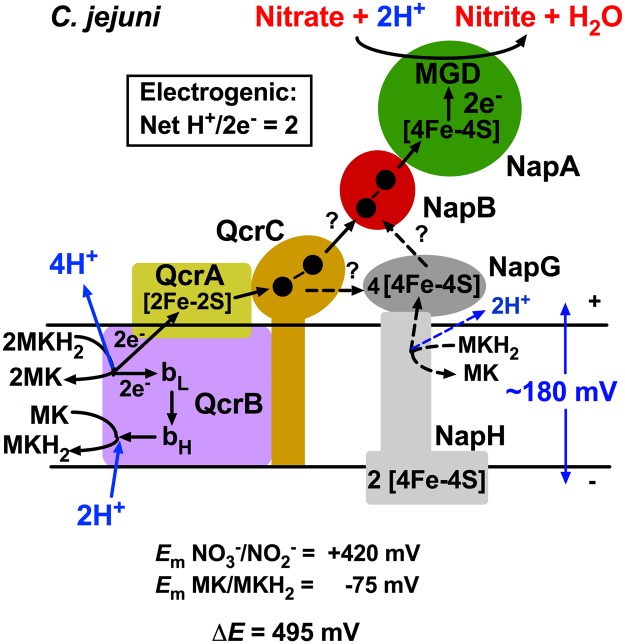
Figure 6.
Model for electrogenic nitrate reduction in C. jejuni. The redox potential span between the MK/MKH2 and the nitrate/nitrite couple is large enough to allow for a Qcr dependent electrogenic mechanism, given a typical transmembrane Δp of ~180 mV. The operation of the Qcr complex directly coupled to the NapAB enzyme gives a net transmembrane proton translocation of 2 H+ per 2e− transferred from menaquinol. There is uncertainty about the precise route of electron transfer from the Qcr complex to NapB (dashed arrows) but the simplest mechanism would be direct transfer from haem 2 of QcrC to haem 1 of NapB. The role of NapG and NapH, which are known to be essential for nitrate respiration, is unclear. NapG may act in the electron transfer pathway itself or NapGH may act as a quinol dehydrogenase involved in a reductive maturation process e.g. for NapA. Black filled circles in QcrC and NapB represent the haems.