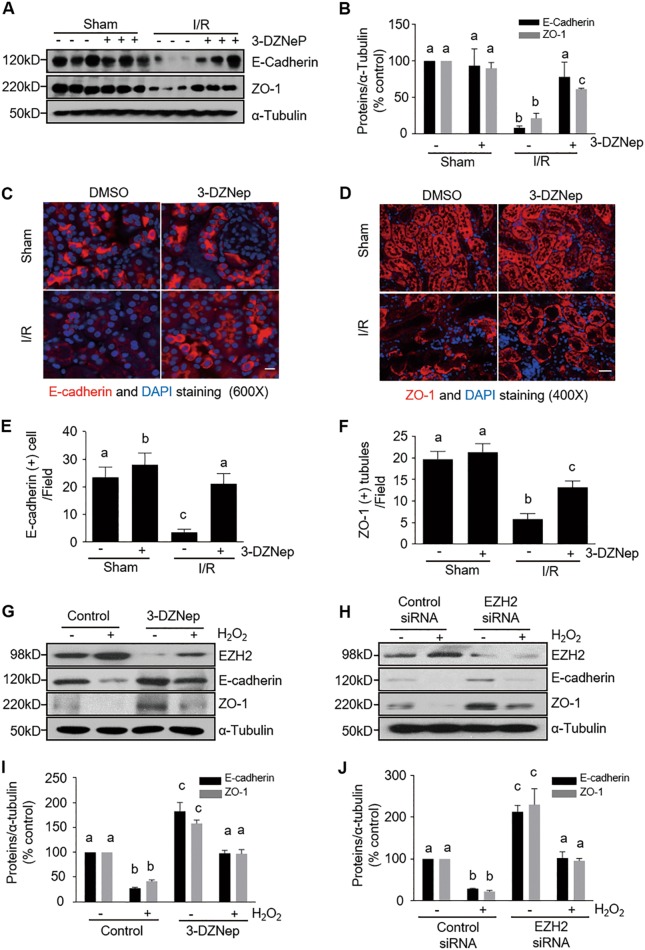
Fig. 5. EZH2 inhibition ameliorates tubular cell adherence and junction damage in the kidney of IR-induced AKI and H2O2-injured TKPT.
a Kidney tissue lysates were subjected to immunoblot analysis with specific antibodies against E-cadherin, ZO-1 and ɑ-tubulin. b Expression levels of E-cadherin and ZO-1 were quantified by densitometry and normalized with ɑ-tubulin. Data are means ± SD. Representative immunoblots are three samples from in each group. Photomicrographs illustrate immunofluorescent staining of E-cadherin (c) (scale bar, 10 µm) or ZO-1 (d) (scale bar, 20 µm) in kidney tissues collected at 48 h after sham and IR injuring with or without 3-DZNep administration in C57/black mice. Tubular cells with positive E-cadherin (e) or ZO-1 (f) staining were counted in 10 high-power fields and expressed as means ± SD. TKPT were pretreated with 5 µM 3-DZNep for 1 h or transfected with control or EZH2 siRNA for 24 h and then exposed to 0.5 mM H2O2 for an additional 12 h. Cell lysates were subjected to immunoblot analysis with specific antibodies against EZH2, E-cadherin, ZO-1, and ɑ-tubulin (g, h) and expression levels of E-cadherin and ZO-1 were quantified by densitometry and normalized with ɑ-tubulin (i, j) as indicated. Data are means ± SD at least three independent experiments. Means with different superscript letters are significantly different from one another (P < 0.05)