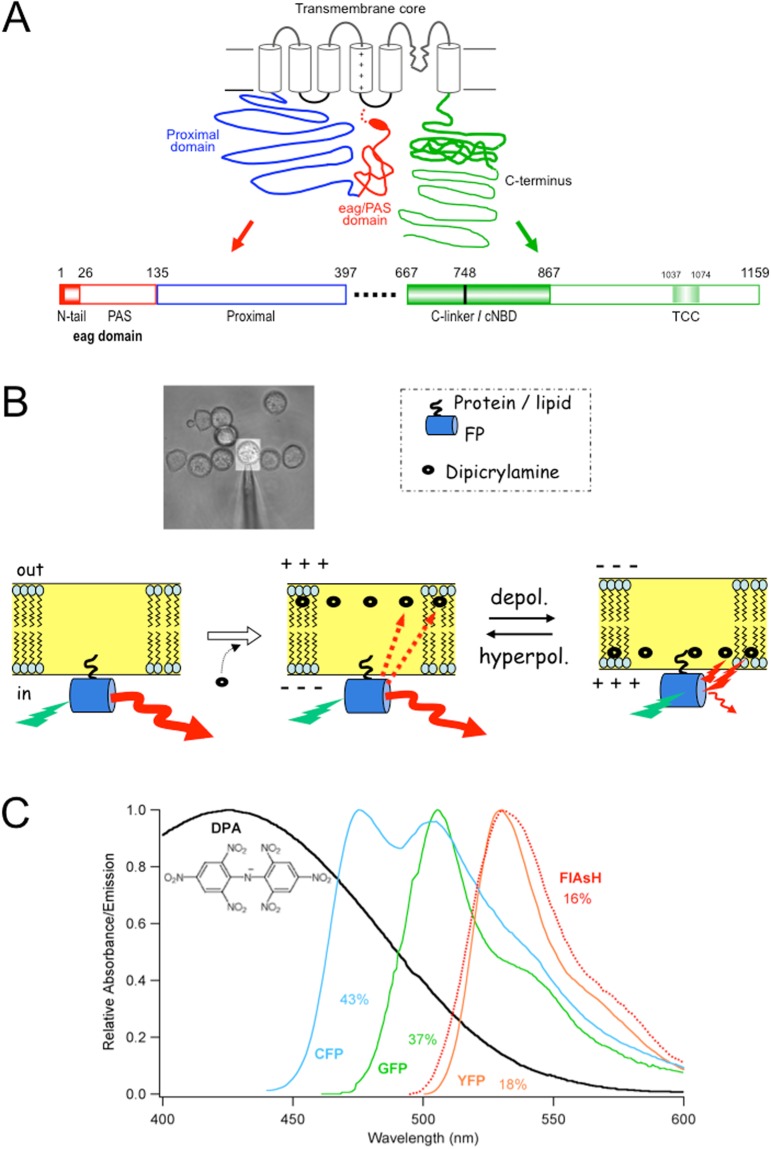
Figure 1.
General topology of a hERG channel α-subunit and schematics of the DPA-based voltage-dependent FRET measurements. (A) Schematic representation of a hERG channel α-subunit indicating the relative positioning of the amino terminal eag/PAS and proximal domains up to the first transmembrane helix, and the C-terminus regions following the sixth transmembrane helix. The N-tail region including an initial flexible segment (dotted line) and the amphipatic α-helix (oval) connecting it to the Per-Arnt-sim (PAS) sub-domain (continuous line) of the eag domain, are depicted in red. The C-terminus is colored green. Linear diagrams of the amino and carboxy termini are shown at the bottom. The size of every segment is represented on a horizontal scale proportional to the total length of the fragments. The numbers correspond to the residues of the hERG sequence marking the boundaries of the different regions. The position of the C-linker/cNBD domains directly linked to the bottom of helix S6 and the location of a proposed tetramerization coiled-coil (TCC) are also shown at the C-terminus. The transmembrane core region containing the six transmembrane helices depicted as cylinders and the corresponding linkers are represented in black. The approximate points of FP insertion used are signaled by asterisks in the upper scheme and placed in their respective position in the lower linear diagrams. (B) Schematic representation of voltage-dependent DPA movements and FRET interactions with membrane-anchored FP fluorophores. An illustration of reversible DPA (black ovals) translocation in response to membrane voltage variations and the corresponding modifications in the fluorescence of an FP (yellow barrel) tag anchored to the internal membrane surface are shown. Different arrow length and thickness are used to highlight the change in fluorescence due to DPA approaching the donor upon depolarization and subsequent decrease of FP fluorescence as a result of increased FRET. A transmission image (40x objective) of the microscope field with the HEK293 cells and recording pipette attached to the selected cell limited by the ViewFinder selection mask (see Methods) is shown in the upper inset. (C) Spectral overlap (%) of CFP, GFP, YFP and FlAsH emission and DPA absorption. The structure of the negatively charged amphiphatic DPA molecule is shown in the inset.