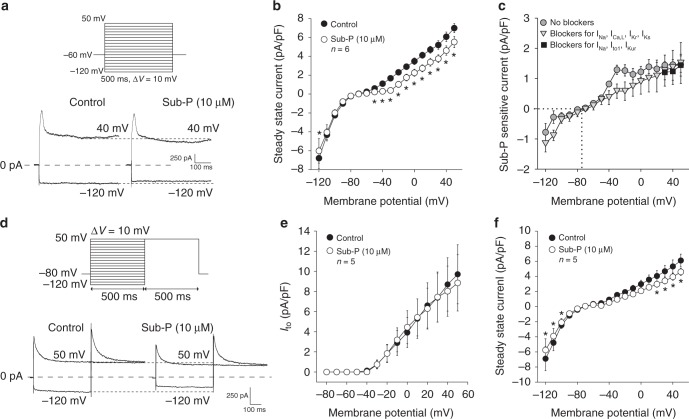
Fig. 2.
Effect of substance-P on steady-state and transient outward currents. a Voltage protocol and current tracings recorded at −120 and +40 mV before (Control) and after application of 10 µM Sub-P. b Average current–voltage relationships of the steady-state current in Control and after application of Sub-P (10 µM) (N = 2, n = 6, two-way RM ANOVA). c Average current–voltage relationships of the Sub-P sensitive current. Sub-P sensitive currents were derived from b (grey filled circles), f (grey filled triangles) and Supplementary Figure 2 (black filled squares), as differential current. d Voltage protocol and transient outward K+ current (Ito) current tracings recorded at −120 and +50 mV before (Control) and after application of Sub-P (10 µM). e Average current–voltage (I–V) relationships of Ito peak currents before (Control) and after application of Sub-P (10 µM) (N = 4, n = 5, two-way RM ANOVA). f Average I–V relationships of steady-state current before (Control) and after application of Sub-P (10 µM) (N = 4, n = 5, two-way RM ANOVA). Blockers for Na+, L-type Ca2+, rapid and slow delayed rectifier K+ currents were present. All values shown are mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05