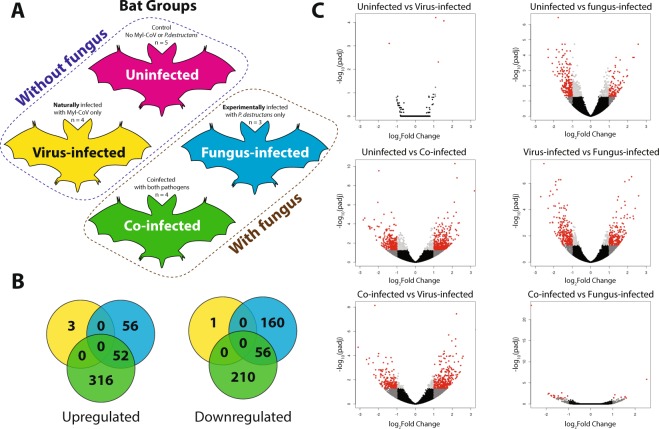
Figure 2.
Co-infection of little brown bats (Myotis lucifugus) with M. lucifugus coronavirus (Myl-CoV) and Pseudogymnoascus destructans results in non-additive patterns of gene expression compared to sole infection with the virus or fungus. (A) Experimental design, showing the four treatments of little brown bat (Myotis lucifugus) established by experimental inoculation with Pseudogymnoascus destructans and by qPCR detection of persistent Myl-CoV infections: uninfected, virus-infected, fungus-infected and co-infected. (B) Differential gene expression identified by DESeq2 among virus-infected, fungus-infected and Co-infected bats as compared to the change each exhibited relative to uninfected bats. (C) Differential gene expression among the four treatments, detected by DESEQ2 and visualized in volcano plots. The log of the adjusted p-value is plotted as a function of the log ratio of differential expression. Colored data points represent different groups of genes based on fold change and false discovery rate (FDR) cutoff; red (>2 fold change, FDR <0.05), dark grey (>2 fold change, FDR > 0.05), light grey (<2 fold change, FDR < 0.05), black (<2 fold change, FDR > 0.05).