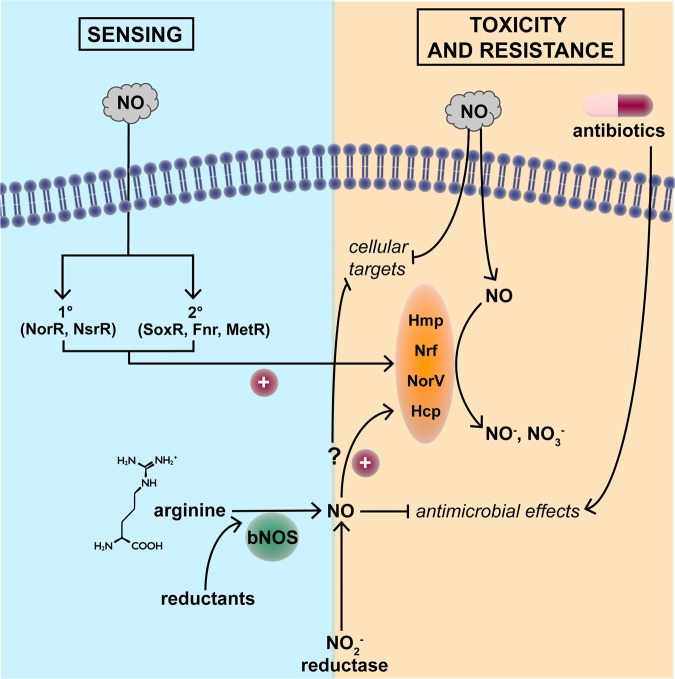
Figure 1. NO sensing and mechanisms of resistance to toxicity.
NO readily enters microbial cells from diverse exogenous sources, but may also be synthesised from arginine by bacterial NO synthase (bNOS). Primary and secondary sensors detect NO, which exerts numerous antimicrobial effects, but paradoxically may protect bacteria from antibiotic action. The toxicity of NO is minimised by NO-detoxifying proteins (Hmp, Nrf, NorV and Hcp). However, it is unclear whether endogenously generated NO elicits equivalent defence responses. For details, see the text.