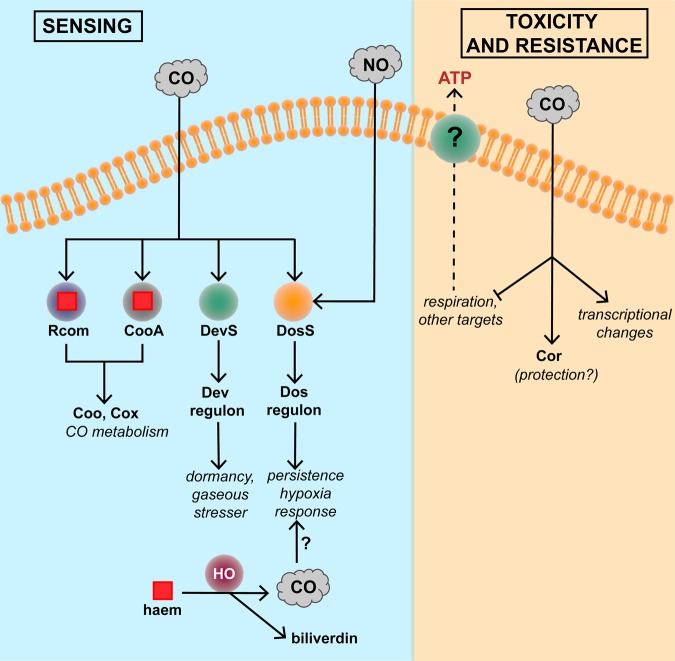
Figure 2. Carbon monoxide sensing and mechanisms of resistance to toxicity.
CO readily enters microbial cells from diverse exogenous sources, but may also be synthesised by endogenous haem oxygenase activity; the role of endogenously derived CO is unclear. Numerous sensors detect CO, leading to CO metabolism or downstream gene regulation. CO exerts numerous antimicrobial effects, but Cor is reported to afford protection. The reported effects of CO on ATP release from bacteria are unexplained. For details, see the text.