Fig. 1.
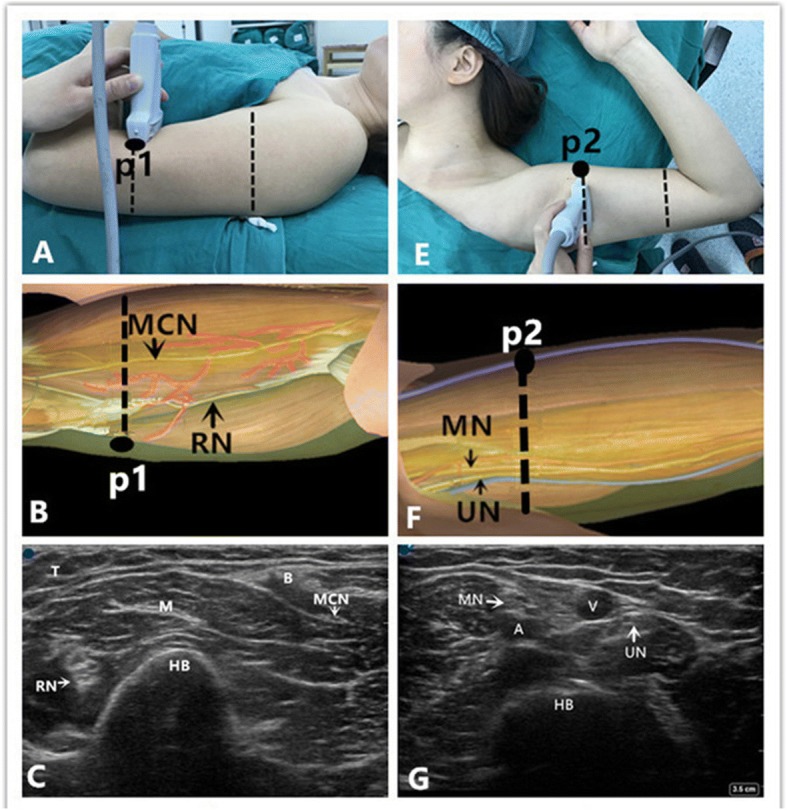
Position of patient, neuroanatomy and ultrasound imaging at the level of upper-median 1/3 and low-median 1/3 of the arm in the operating room. a Position of the patient, the probe, and the needle (“p1”) during block of the radial and musculocutaneous nerve. b Topography of the radial nerve (RN) and the musculocutaneous nerve (MCN); red = muscular branches; and the black point “p1”denotes the puncture site. The dotted line denotes the probe position. c Ultrasound depiction of the radial nerve (RN) and the musculocutaneous nerve (MCN). The blue point is situated at the lateral side of the probe. The RN is round with a hyperechoic structure and is located between brachialis and humerus laterally. The MCN is fusiform with a hyperechoic structure, and is located between biceps and brachialis close medially. Also note the humerus (HB), and the triceps (T), biceps (B), and brachialis (M) muscles. e Position of the patient, the probe, and the needle (“p2”) during block of the median, ulnar, and medial antebrachial cutaneous nerves. f Topography of the median nerve (MN), the ulnar nerve (UN). The black point “p2”denotes the puncture site. The dotted line denotes the probe position. g Ultrasound description of the median nerve (MN) and the ulnar nerve (UN). The blue point is situated at the cephalic side of the probe. The MN is between 12 and 1 o’clock in relation to the humeral artery. The UN is situated at the 3 o’clock position of the basilic vein, brachial artery (A), basilic vein (V), and humerus (HB)
