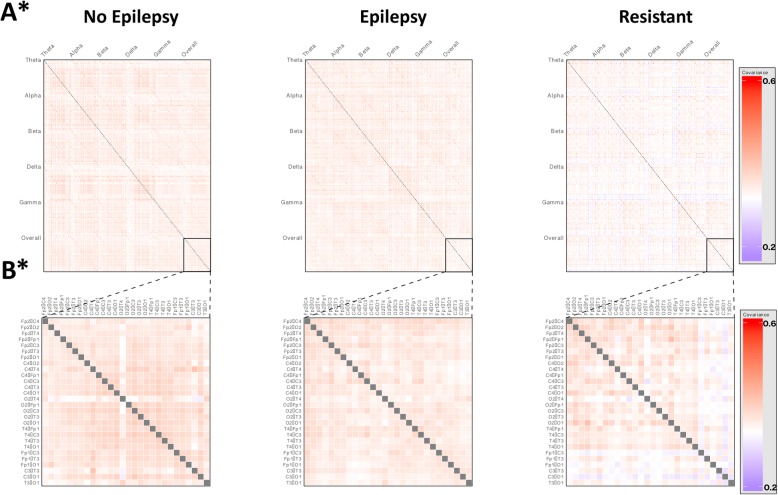
Fig. 7.
Epilepsy status groups are differentiated by electrophysiological measures. All subplots depicting a statistical comparison significant at a p value of < 0.05 are marked with an asterisk (*). a Covariance matrices of inter-electrode coherence measurements for No Epilepsy (n = 18, green), Epilepsy (n = 16, blue) and Resistant (n = 8, red) groups, allowing visualisation of higher-order network function. Each row and each column represent a pair of electrodes. These are arranged into blocks along the axes, with measures for each electrode pair at all frequency bands and across the overall spectrum. The intensity of each cell represents the covariance between activity in the corresponding electrode pairs at the corresponding frequency band. Visualisation suggests differences in network activities between epilepsy groups; comparison of first principal components indicated a statistically significant difference between groups (p < 0.05, Kruskal-Wallis H test), indicating that there are differences in network architecture between epilepsy groups. b Subplots of overall covariance matrices in A, showing only covariance between electrode pairs over the whole power spectrum. Each row and each column represents an electrode pair as labelled. Closer examination of covariance within the overall spectrum suggests that differences seen across the whole matrix are still evident within the overall spectrum alone