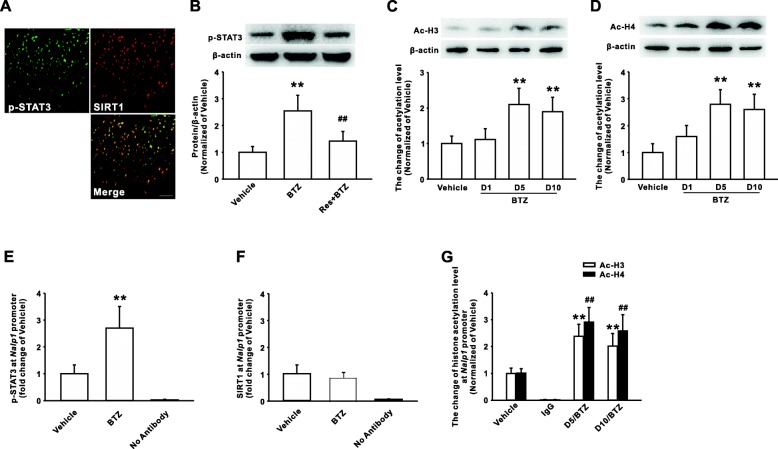
Fig. 4.
P-STAT3, but not SIRT1, directly mediated the expression of NALP1 following bortezomib treatment. a The photographs show double staining between SIRT1 (red) with NALP1 (green) in spinal dorsal horn on day 10 following bortezomib treatment. n = 4 in each group; scale bar, 50 μm. b Application of resveratrol (i.t.) reduced the increase of p-STAT3 on day 10 following BTZ treatment. n = 6 in each group, **P < 0.01 versus the vehicle group, ##P < 0.01 versus the corresponding BTZ group. BTZ treatment significantly increased the global acetylation of histone H3 (K9) (c) and H4 (K16) (d) in spinal dorsal horn of rats. n = 6 in each group, **P < 0.01 versus vehicle group. e ChIP results showed the enhanced recruitment of p-STAT3 to Nalp1 gene promoter on day 10 following BTZ treatment. n = 5 in each group, **P < 0.01 versus vehicle group. f The recruitment of SIRT1 to Nalp1 gene promoter did not significantly changed on day 10 in spinal dorsal horn of rats with bortezomib treatment. n = 5 in each group, **P < 0.01 versus vehicle group. g ChIP assay showed BTZ treatment increased the acetylation of histone H3 and H4 on Nalp1 gene promoter region flanking p-STAT3-binding site in rats. n = 6 in each group, **P < 0.01 versus corresponding vehicle group, ##P < 0.01 versus the corresponding vehicle group