Fig. 4.
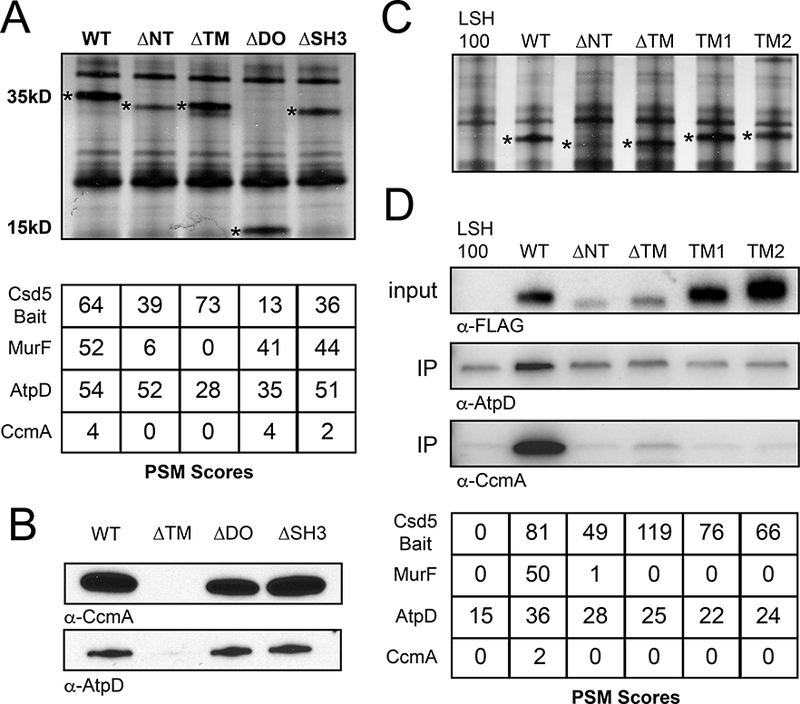
Csd5 N-terminal and transmembrane domains promote protein-protein interactions with MurF, CcmA, and ATP Synthase.
A. Top: Silver stain of Csd5 domain deletion immunoprecipitation (IP) fractions. Bait proteins indicated with an asterisk. Bottom: Mass spectrometry positive spectral match (PSM) counts for indicated Csd5–2X-FLAG domain deletion bait proteins, CcmA, and MurF from Csd5 domain deletion IPs; WT (KBH127), ΔNT (KBH128), ΔTM (KBH129), ΔDO (KBH132) and ΔSH3 (KBH133).
B. Immunoblot detection of CcmA and AtpD in IPs of indicated Csd5 deletion variants using α-CcmA and α-AtpD antibodies respectively.
C. Silver stain of Csd5 N-terminal deletions and Csd5-TlpC transmembrane chimera IP fractions. TM1 (KBH169), TM2 (KBH170). Bait proteins indicated by an asterisk.
D. Top: Immunoblot detection of AtpD and CcmA in input and IP fractions of indicated Csd5 variants using α-CcmA and α-AtpD antibodies; Csd5 variants detected in the input fractions with α-FLAG antibody. Bottom: Mass spectrometry PSM counts for Csd5 bait proteins, MurF, AtpD and CcmA in the indicated IP fractions.
