Figure 1. Fibrinogen (Fg) induced activation of astrocytes.
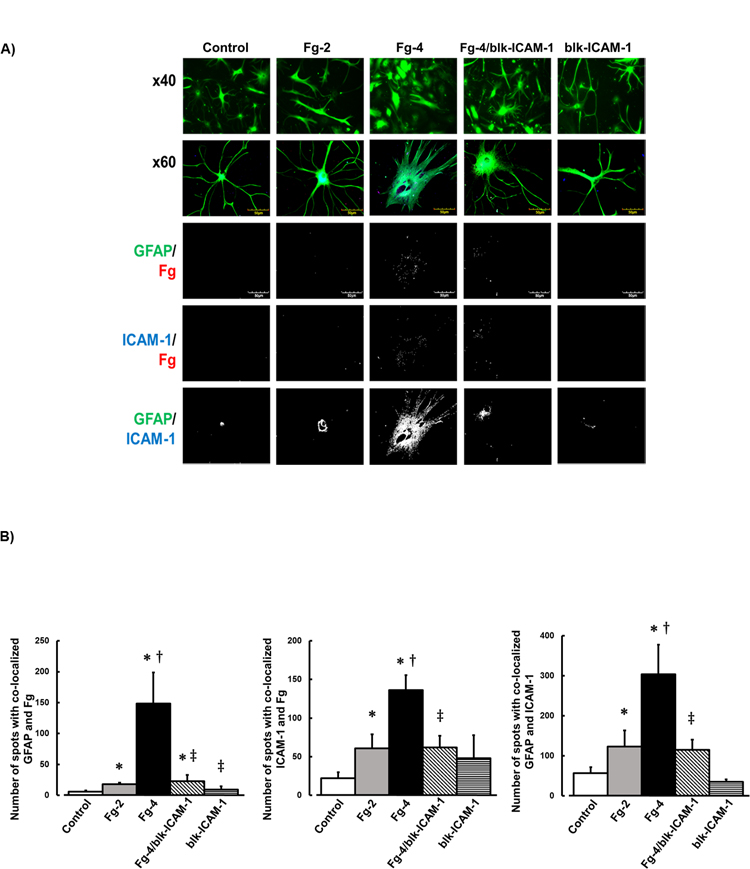
A) Examples of images of cultured mouse brain astrocytes treated with serum free media alone (control), 2 mg/ml of Fg (Fg-2), 4 mg/ml of Fg (Fg-4), 4 mg/ml of Fg in the presence of function blocking anti-intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) antibody (Fg-4/blk-ICAM-1), or with function blocking anti-ICAM-1 antibody alone (blk-ICAM-1).
Astrocytes were identified by expression of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP, green); ICAM-1 is shown in blue, and Fg -red.
First row: images taken with objective x40. Rows 2–5: images taken with objective x60. Rows 3–5: represent images after deconvolution.
Fg dose-dependently activated astrocytes (see shape change and retraction of processes), increased association of Fg with astrocytes and with ICAM-1, and increased expression of ICAM-1 in astrocytes.
B) Summary of number of spots with co-localized GFAP and Fg (GFAP/Fg); ICAM-1 and Fg (ICAM-1/Fg), and GFAP and ICAM-1 (GFAP/ICAM).
P < 0.05 for all. * - vs. Control, †- vs. Fg-2, ‡- vs. Fg-4; n=4
