Figure 3. Impaired sensing of HBV infection at high MOIs or early time points of infection.
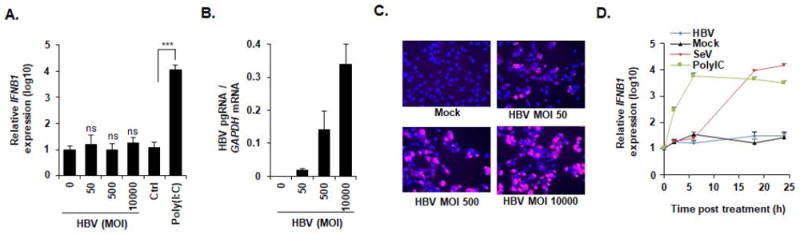
(A-C) HepG2-NTCP cells were infected with HBV at increasing MOIs (0, 50, 500, and 10000 GEq/cell) or transfected with Poly (I:C) (100 ng). Two days after infection or transfection, cells were lysed, total RNA was extracted, and IFNB1 expression (A) as well as HBV pgRNA levels (B) were quantified by qRT-PCR. (A) Results are expressed as means ± SD relative IFNB1 expression (log10) compared to mock infected cells (MOI 0, set at 1) from three independent experiments performed in triplicate. (B) Results are expressed means ± SD relative HBV pgRNA levels compared to mock infected cells (MOI 0, set at 100%) from three independent experiments performed in triplicate. Alternatively, HBV infection was assessed at 10 days post infection by IF of HBsAg (C). One representative experiment is shown. (D) HBV infection does not induce IFNB1 expression at early time points. HepG2-NTCP cells were either infected by HBV or SeV, or transfected with Poly (I:C). Total RNA was extracted at 2 h, 6 h, 18 h, and 24 h post infection/transfection and IFNB1 expression was assessed by qPCR. Results are expressed as means ± SD relative IFNB1 expression (log10) compared to naive cells (0, set at 1) from three independent experiments performed in triplicate.
