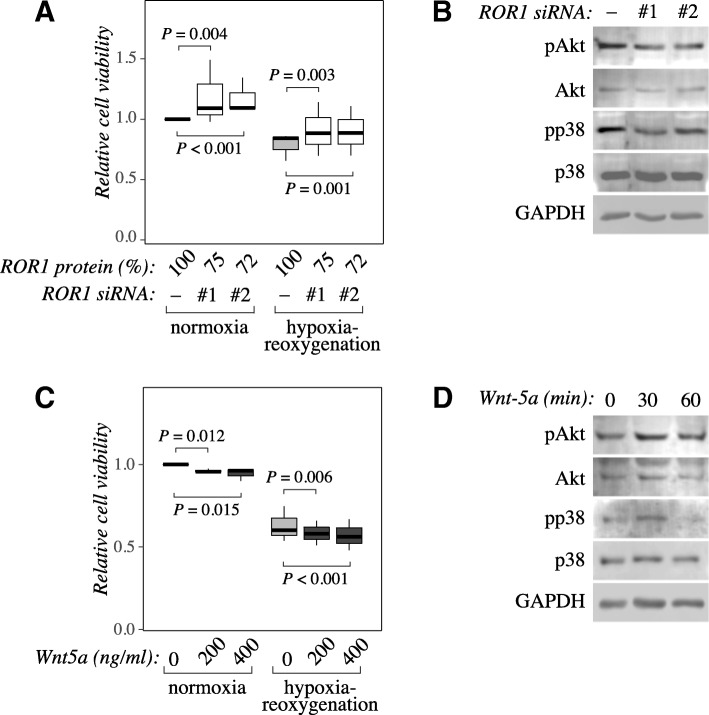
Fig. 5.
ROR1 knockdown reduces but Wnt-5a ligand treatment increases cardiomyocyte viability under normoxia and hypoxia-reoxygenation. a HL-1 cells were transfected with two different siRNAs targeting ROR1 (ROR1 siRNA #1 and #2) or negative control siRNA. Twenty-four hours after transfection, cells were either transferred into a hypoxic work station (1% O2) or were maintained in normoxia as controls. After another 24 h, all cells were returned to normoxia for 24 h to allow for reoxygenation. Cell viability was analyzed using the MTT assay. A box plot presentation is shown indicating cell viability as normalized to negative control siRNA-treated cells cultured in normoxia. The efficacy of the ROR1 siRNAs in down-regulating ROR1 expression is indicated (ROR1 protein %). Three independent experiments each including six replicates were carried out. b Western analysis of total and phosphorylated Akt and p38 in HL-1 cells lysed 48 h after siRNA transfection. c HL-1 cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of Wnt-5a since plating. Twenty-four hours after plating, cells were either transferred into a hypoxic work station (1% O2) or were maintained in normoxia as controls. After another 48 h, all cells were returned to normoxia for 24 h to allow for reoxygenation. Cell viability was analyzed using the MTT assay. A box plot presentation is shown indicating cell viability as normalized to cells cultured in the absence of the ligand in normoxia. Three independent experiments each including three replicates were carried out. d Western analysis of total and phosphorylated Akt and p38 in HL-1 cells treated or not with 400 ng/ml of Wnt-5a for 30 or 60 min. Negative control cells were lysed at the same time as the 30-min sample