Figure 1.
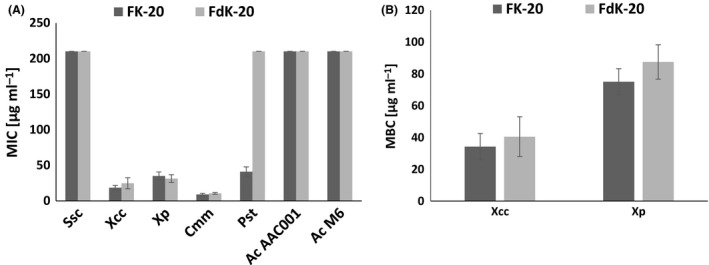
Bacteriostatic and bactericidal effects of RPMs towards several plant pathogenic bacteria.
A. Growth inhibition activity (minimal inhibitory concentration, MIC) of FK‐20 and FdK‐20 RPMs towards different bacteria after 24 h incubation at 28°C: Ssc, Streptomyces scabies Av; Xcc, Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris ATCC 33913; Xp, Xanthomonas perforans 97‐2; Cmm, Clavibacter michiganensis subsp. michiganensis NCPPB 382; Pst, Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000; Ac AAC001, Acidovorax citrulli AAC00‐1; and Ac M6, A. citrulli M6.
B. Bactericidal effect (minimal bactericidal concentration, MBC) of FK‐20 and FdK‐20 RPMs towards Xcc ATCC 33913 and X. perforans 97‐2 after 24 h incubation at 28°C. The highest concentration tested was 200 μg ml−1; therefore, values ~200 μg ml−1 mean that no inhibitory effect was detected under tested conditions. Data represent averages and standard errors of at least three independent experiments with three replicates for each peptide/bacterial strain combination.
