Fig. 3.
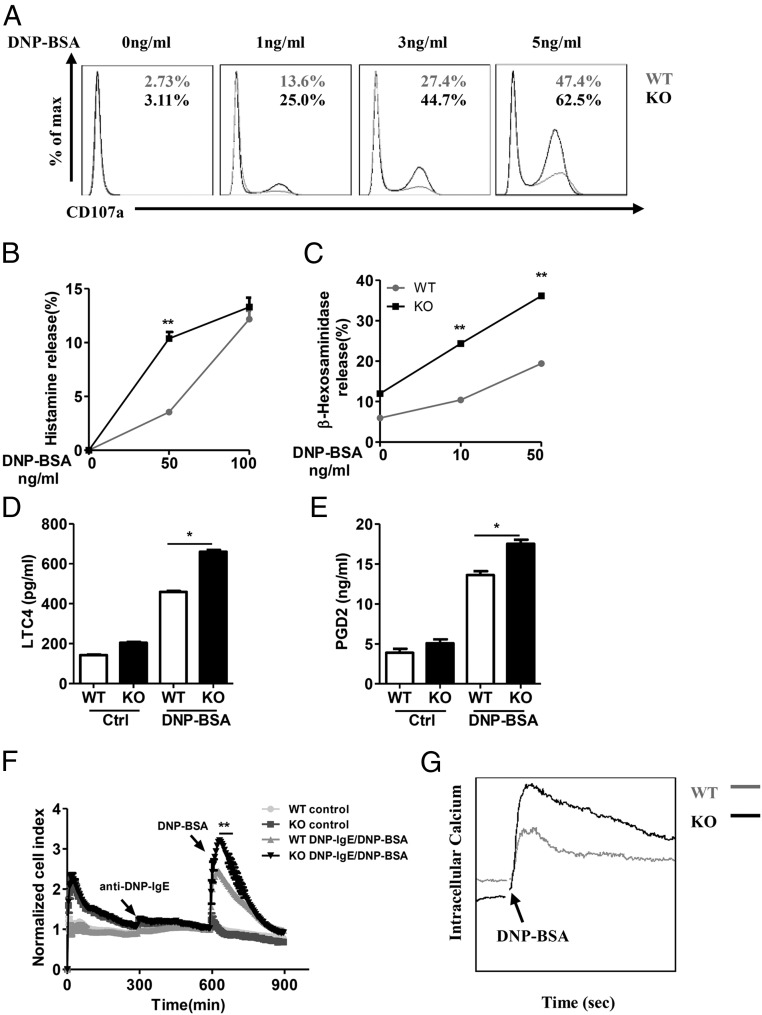
RKIP deficiency promotes IgE−FcεRI-mediated degranulation in mast cells. (A) The WT and RKIP KO BMMCs were presensitized with 1 μg/mL of anti–DNP-IgE overnight and activated with the indicated concentrations of DNP-BSA for 10 min. The BMMCs were incubated with anti-mouse CD107a, c-Kit, or FcεRI antibodies and then subjected to FACS analysis. C-Kit and FcεRI double-positive cells were gated out as BMMCs, and degranulation was assessed by CD107a expression levels on BMMCs. The numbers in the graphs indicate the percentages of CD107a+ cells. (B) WT and RKIP KO BMMCs were presensitized with 1 μg/mL of anti–DNP-IgE overnight and activated with the indicated concentrations of DNP-BSA for 1 h, and the secretion of histamine was determined by ELISA. Degranulation was assessed by histamine release (presented as percentages of total histamine content). (C) BMMCs were presensitized with 1 μg/mL of anti–DNP-IgE IgE overnight and activated with the indicated concentrations of DNP-BSA for 30 min; degranulation was assessed by measuring β-hexosaminidase levels. (D and E) The WT and RKIP KO BMMCs were presensitized with 1 μg/mL of anti–DNP-IgE overnight and activated with 100 ng/mL of DNP-BSA for 1 h; the release of the (D) LTC4 and (E) PGD2 was measured by competitive ELISA (Cayman Chemicals). (F) Measurement of IgE−FcεRI-mediated cell electrical impedance. The WT and RKIP KO BMMCs were seeded onto the fibrinogen-coated surfaces of microelectronic cell sensor arrays integrated into the bottoms of microtiter plates and presensitized with 1 μg/mL of anti–DNP-IgE for 5 h. Subsequently, the cells were stimulated with 100 ng/mL of DNP-BSA, with the impedance being measured every 5 min and then analyzed by xCELLigence (a real-time cell analyzer). (G) Calcium flux was measured at the indicated times after 1 μg/mL of anti–DNP-IgE presensitization and DNP-BSA stimulation in the WT and RKIP KO BMMCs. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01. Data are representative of the three experiments. Data represent mean and SD.