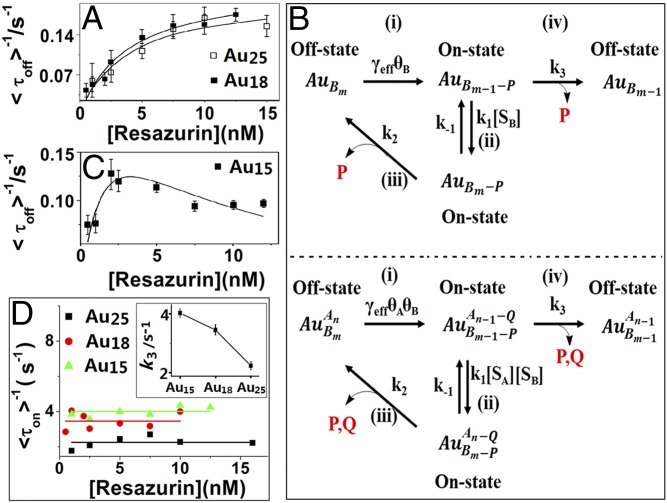
Fig. 3.
Kinetic study of different-sized Au clusters. (A and C) Resazurin concentration titrations of <τoff>−1 on Au25 (A), Au18 (A), and Au15 (C) with 20 mM NH2OH. Each data point is averaged over the turnover trajectories of >50 clusters, with SEM as the error bar. The solid lines are fittings with Eqs. 1 (A) and 3 (C), respectively, with parameters summarized in SI Appendix, Table S1. (B, Top) Noncompetitive Langmuir−Hinshelwood mechanism of catalysis on a single nanoparticle. (B, Bottom) Competitive Langmuir−Hinshelwood mechanism of catalysis on a single nanoparticle. [A], the substrate NH2OH concentration; [B], the substrate resazurin concentration; Au, Au nanoparticle; P, the product resorufin; Q, the product from NH2OH. γeff represents the combined reactivity of all surface catalytic sites of a nanoparticle. k1, k−1, k2, and k3 are the rate constants at each steps. θ is the fraction of catalytic sites that are occupied by substrates. (D) Resazurin concentration dependence of <τon>−1 of Au15, Au18, and Au25. The solid lines are the fittings with constants. Inset is the size dependence of k3.