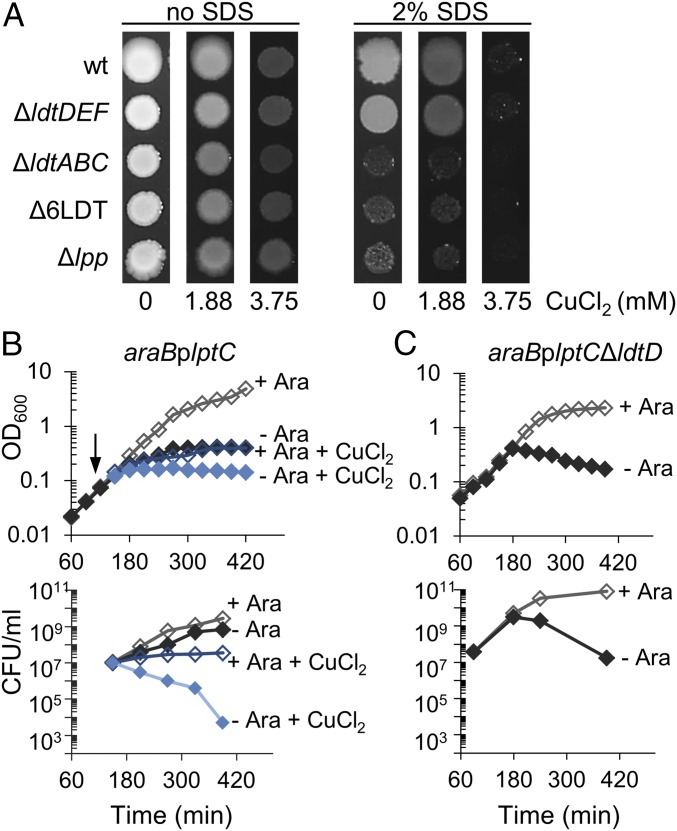
Fig. 1.
Copper impairs the robustness of the cell envelope. (A) Growth in presence of SDS and copper. Overnight cultures of E. coli BW25113 (wt), BW25113ΔldtDΔldtEΔldtF (ΔldtDEF), BW25113ΔldtAΔldtBΔldtC (ΔldtABC), BW25113Δ6LDT, and BW25113Δlpp were adjusted to an equal OD and serial dilutions were spotted on plates with or without 2% SDS, containing no CuCl2, 1.88 mM or 3.75 mM CuCl2 (0, 0.25, and 0.5× MIC, respectively). Plates were incubated at 37 °C for 48 h. Representative results of three independent experiments are shown. Spots of the 10−3 dilution are shown; the complete spot plate assay is shown in SI Appendix, Fig. S1B. (B) Copper induces cell killing when the transport of LPS to the OM is compromised. Cells of the strain araBplptC were grown to an OD600 of 0.2 under permissive conditions (LD medium in the presence of 0.2% arabinose). Cells were harvested, washed three times in LD and diluted 1/100 in LD medium + 0.2% Ara and LD medium without Ara. When cells reached an OD600 of 0.1 the cultures were split and 3.75 mM CuCl2 was added (arrow). Cell growth was monitored by OD600 measurements (Upper) and viability was assessed by determining CFU (Lower). Results of the wild-type strain are shown in SI Appendix, Fig. S2. (C) An ldtD mutant loses viability upon lptC depletion. Growing cells of the araBplptCΔldtD were shifted into media with or without arabinose and the OD (Upper) and viability (Lower) was followed. The ldtD mutant lysed and lost viability in the absence of arabinose, similar to the LdtD-containing wild-type cells grown in the presence of copper chloride (B), suggesting that LdtD is inhibited by copper chloride.