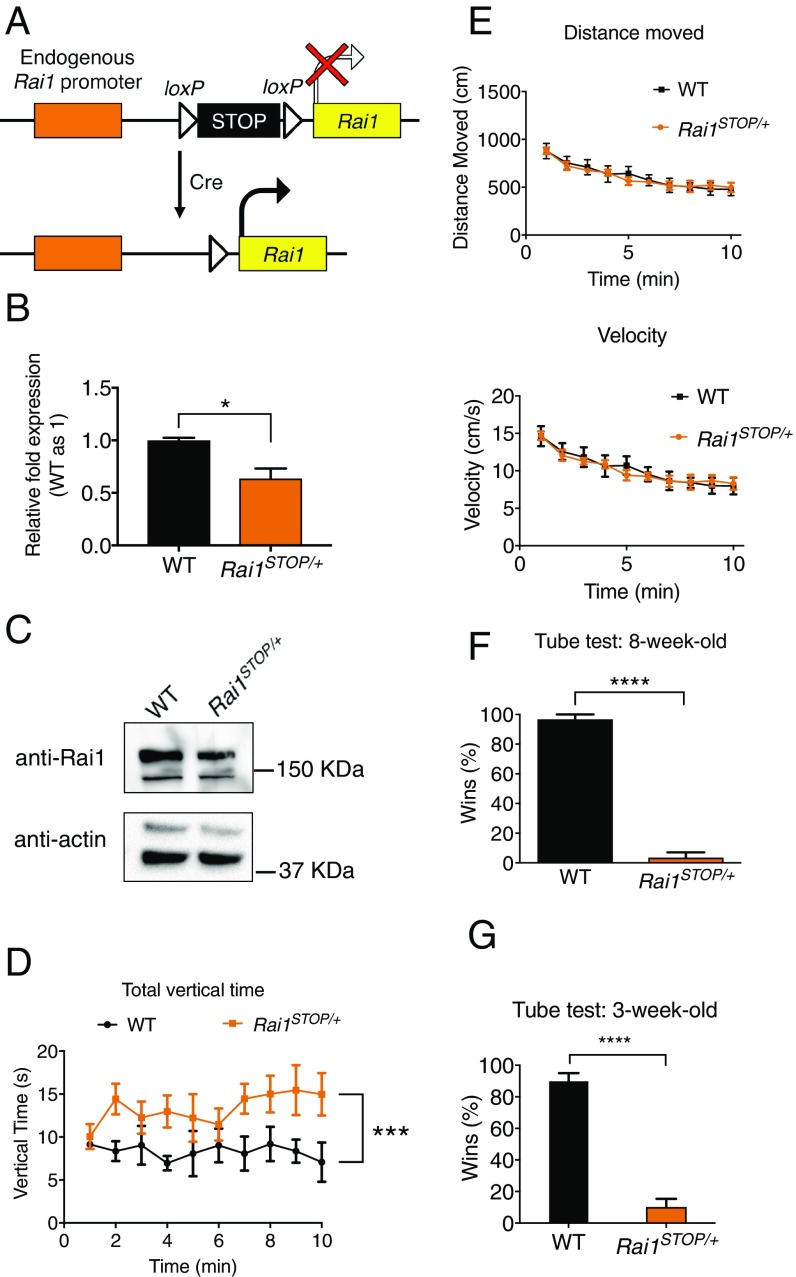
Fig. 1.
Rai1STOP/+ mice display increased rearing and social interaction deficits. (A) Schematic showing the strategy to conditionally reactivate Rai1 expression. (B) Quantitative RT-PCR showing decreased Rai1 mRNA expression in the Rai1STOP/+ brains (n = 3; mean ± SEM; *P < 0.05; t test). (C) Western blot showing a decreased Rai1 protein expression in the Rai1STOP/+ brain. (D) Rai1STOP/+ mice showed increased rearing in the activity chamber (mean ± SEM; ***P < 0.001; two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey post hoc test; for D–F, WT mice, n = 5; Rai1STOP/+ mice, n = 7). (E) Travel distance and velocity in the activity chamber were not significantly different between WT and Rai1STOP/+ mice (mean ± SEM; P > 0.05; two-way ANOVA). (F) Rai1STOP/+ mice showed a severe social interaction deficit in the tube test (mean ± SEM; ****P < 0.0001; t test). (G) Juvenile Rai1STOP/+ mice showed abnormal social interaction in the tube test (n = 7 for each genotype, mean ± SEM; ****P < 0.0001; t test).