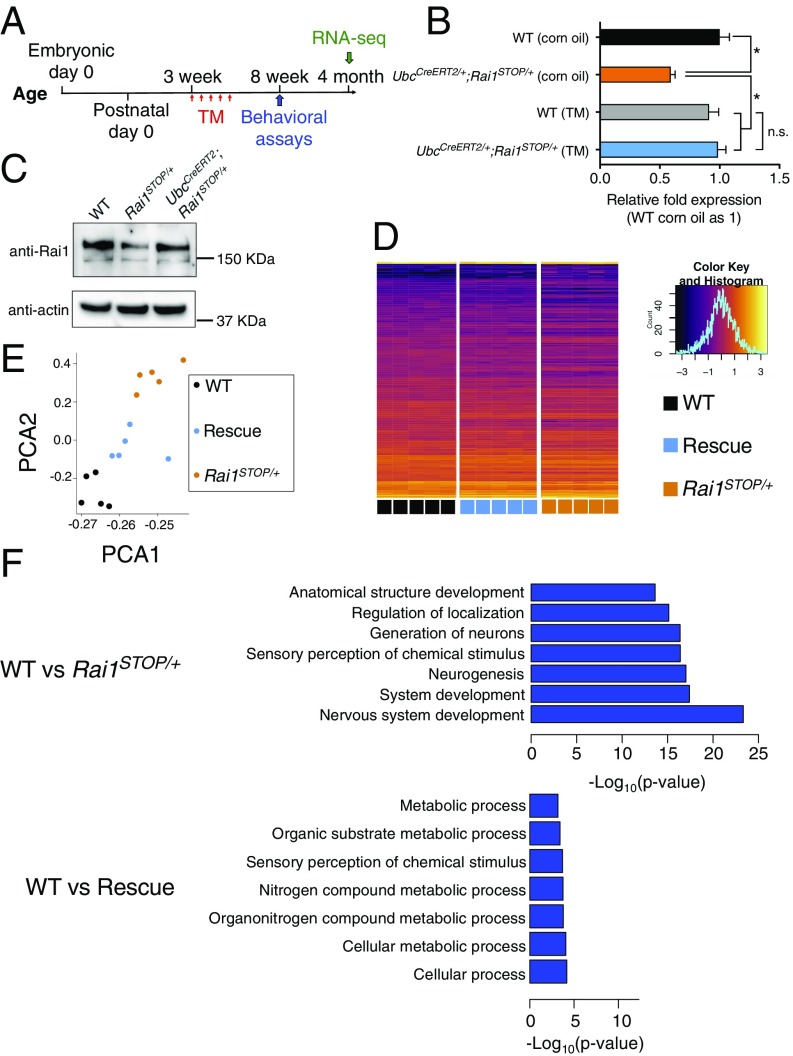
Fig. 2.
Reactivation of Rai1 in juvenile mice partially rescued transcriptional deficits. (A) Time line for TM injections, behavioral assays (Fig. 3), and RNA-seq experiments. (B) Quantitative RT-PCR showing that the Rai1 level was restored to the WT level in a Cre-dependent manner (n = 3; mean ± SEM; *P < 0.05, n.s., not significant; one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey post hoc test). (C) Western blot showing that decreased Rai1 protein level was normalized by TM treatment. (D) Hierarchical clustering of DEGs across genotypes, with each row representing individual genes and each column representing each sample (Inset: x axis represents the z-score; y axis represents the count in each bin of the histogram). (E) Principal component analysis of DEGs showing that the rescued transcriptomes move closer to WT transcriptomes. Each dot represents one mouse. (F) GO analysis using DEGs suggests that the genes involved in neurodevelopment were among the most misregulated in the Rai1STOP/+ brains (for full lists, see SI Appendix, Fig. S3A and Datasets S1 and S2).